Week 2 Worklog
Week 2 Objectives:
- Learn fundamental AWS networking concepts (VPC, Subnets, Routing, Security, Connectivity).
- Understand how to manage traffic flow and secure workloads inside VPC.
- Gain insights into AWS connectivity options (Peering, Transit Gateway, VPN, Direct Connect).
- Explore Elastic Load Balancing for distributing application traffic.
Tasks to be carried out this week:
| Day | Task | Start Date | Completion Date | Reference Material |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-3 | - Study AWS Networking – VPC & Core Concepts: • Amazon VPC • Subnets • Route Tables • Internet Gateway • Elastic Network Interface (ENI) • Interface Endpoint • Gateway Endpoint • Security Group • Network ACL • VPC Flow Logs • VPC Peering • Transit Gateway • VPN Site-to-Site • AWS Direct Connect • Elastic Load Balancing | 09/15/2025 | 09/17/2025 | AWS Study Group |
| 4 | - Practiced AWS Networking Labs: created and configured VPCs, subnets, route tables, security groups, and internet gateways | 09/18/2025 | 09/18/2025 | AWS Study Group |
| 5 | - Practice AWS Networking Labs: Create EC2, test connect by using MobaXterm and putty, create NAT gateway | 09/19/2025 | 09/19/2025 | EC2 |
Week 2 Achievements
1 Studied Amazon VPC & Networking concepts, including:
CloudCity – Analogy for the Entire VPC
Imagine the components in a VPC as a city.
- Amazon VPC – The City
- VPC = the city you build in the cloud.
- Has a fixed area (CIDR block).
- You own the whole infrastructure, divide it into districts, and manage traffic.
- Subnets – Neighborhoods
- Subnet = a neighborhood inside the city.
- Each neighborhood belongs to one district (Availability Zone).
- Public neighborhoods (connected to the highway) vs. private neighborhoods (internal only).
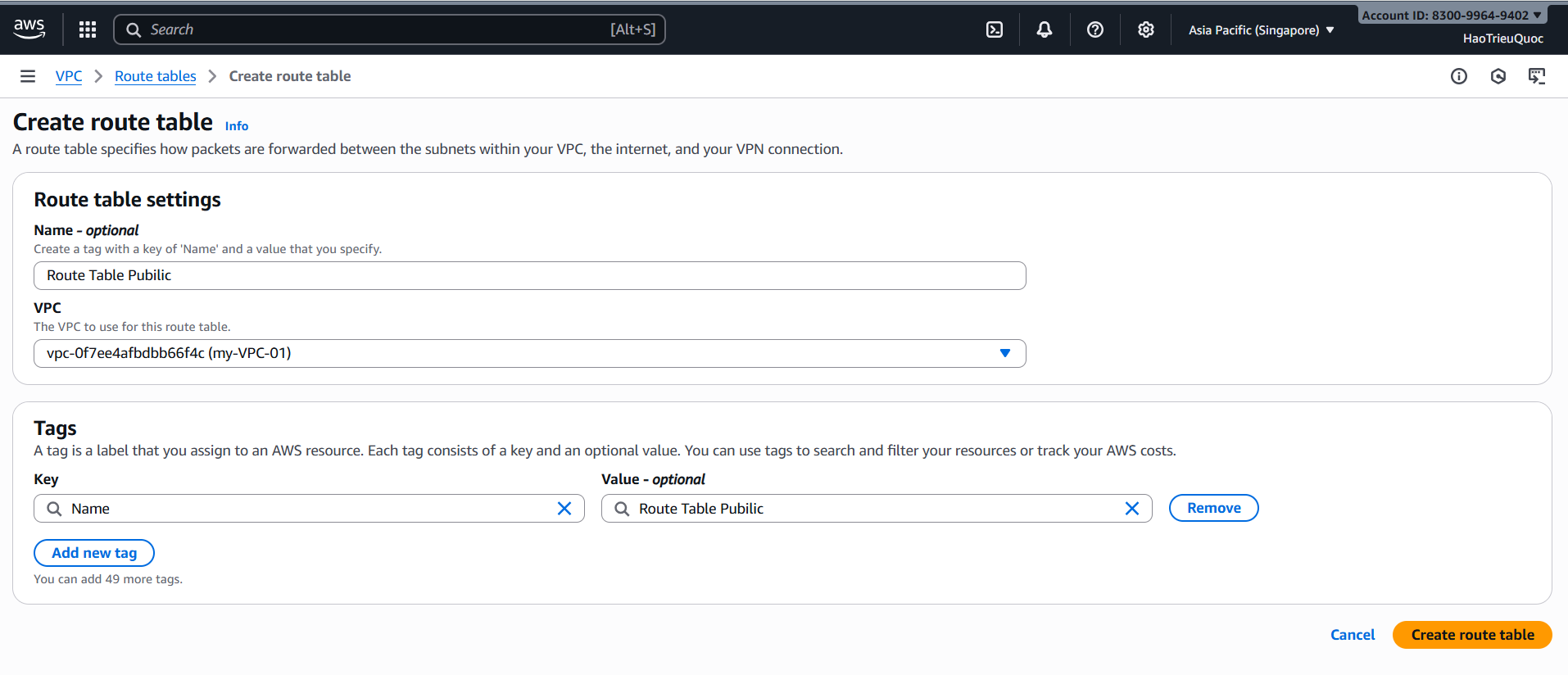
- Route Tables – Maps
- Route table = the map of each neighborhood.
- Shows where traffic goes: “to the internet → through IGW”, “internal traffic → local route”.
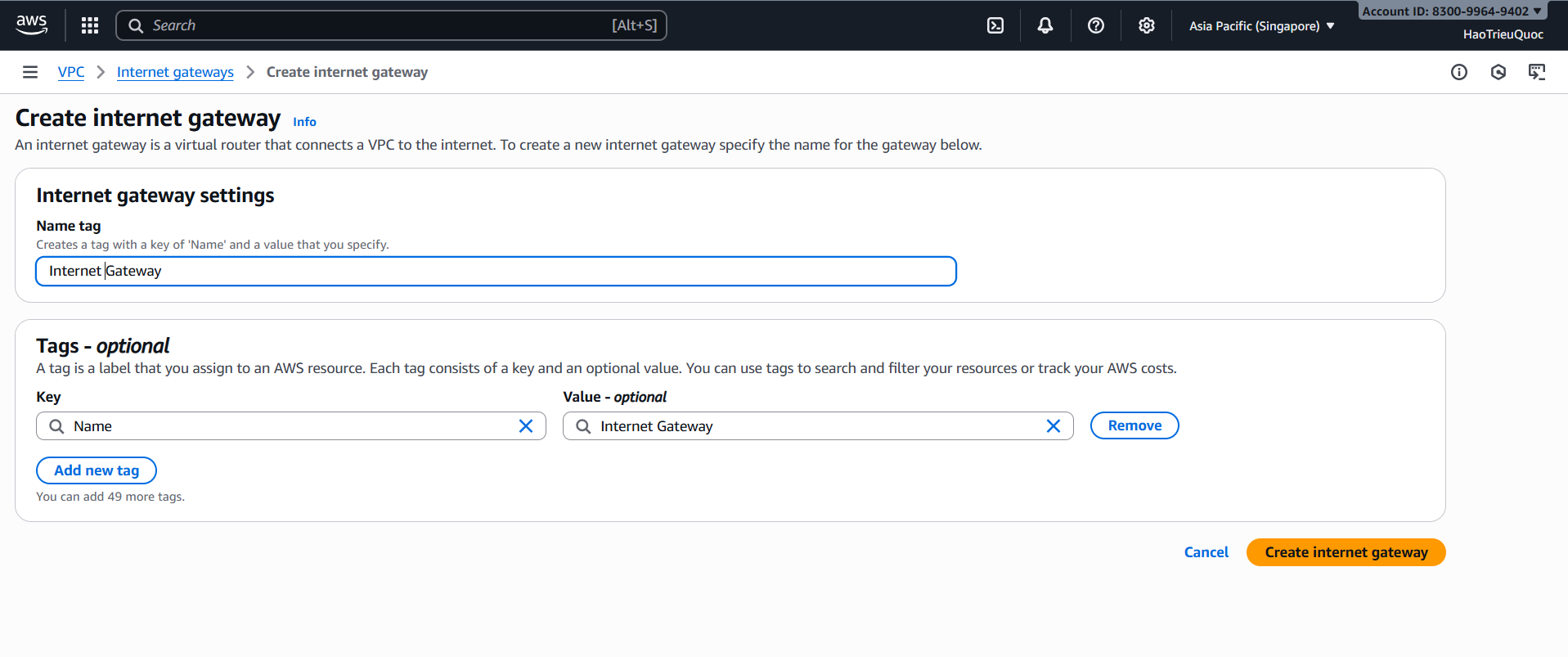
- Internet Gateway (IGW) – International Border Gate
- IGW = the international border gate connecting the city to the outside world (Internet).
- Only citizens with passports (Public IP/Elastic IP) can pass through.
- Elastic Network Interface (ENI) – The Door to a House
- ENI = the door of each apartment (instance).
- Each door has a number (IP).
- The door can be detached and attached to another house in the same district (AZ).
- Interface Endpoint – VIP Tunnel
- Interface Endpoint = a VIP tunnel inside the neighborhood.
- Leads directly to government offices/services (S3, Systems Manager, CloudWatch, SaaS vendors).
- No need to go through the border gate (IGW).
- Protected by its own Security Group.
- Gateway Endpoint – Special Toll Booth
- Gateway Endpoint = a toll booth inside the city.
- Connects only to two special places: the warehouse (S3) and the marketplace (DynamoDB).
- Uses internal roads, no need to reach the highway.
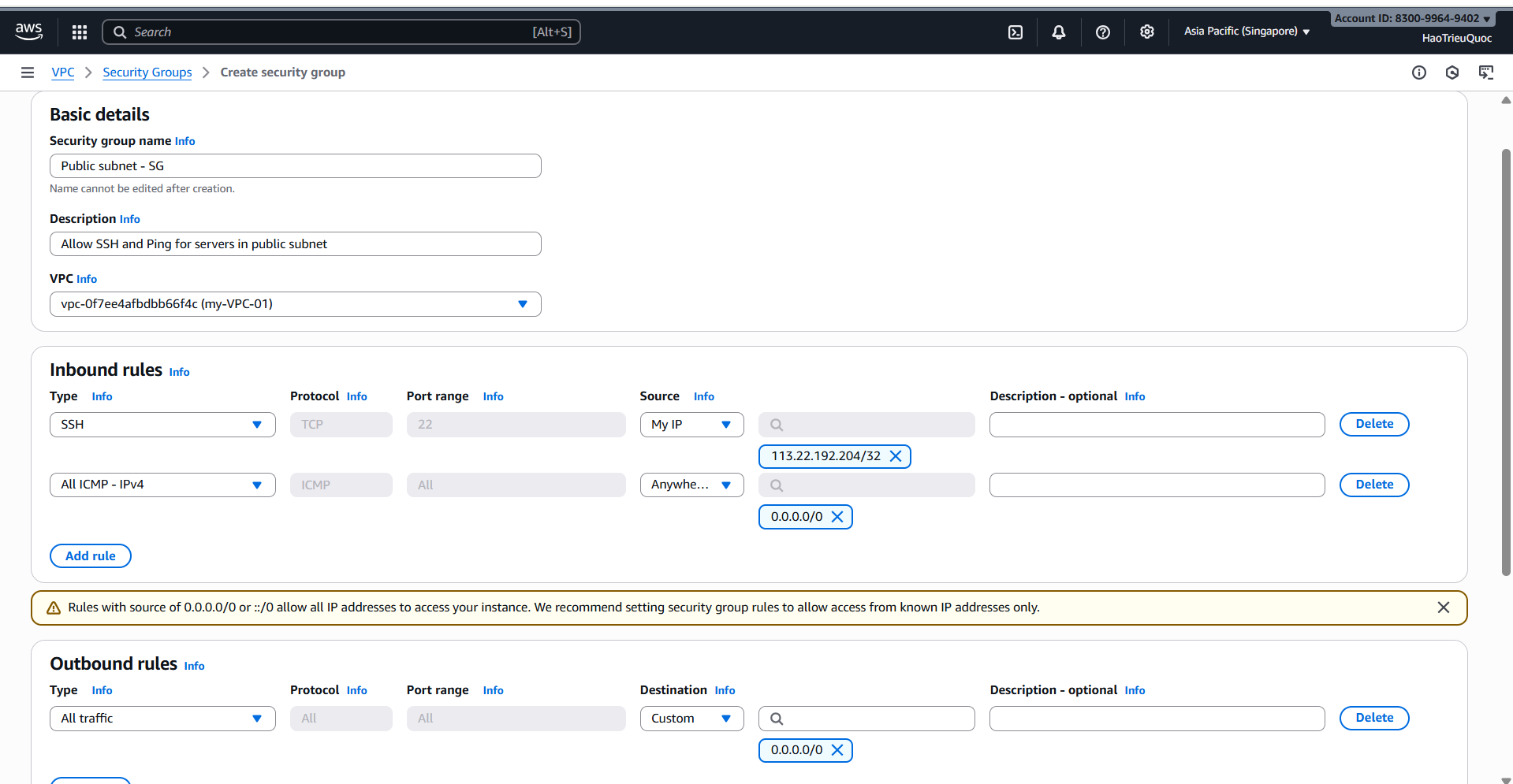
- Security Group – Door Guards
- Security Group = guards standing at the door of each house (ENI).
- They decide who can enter/exit.
- Rules are stateful: if entry is allowed, return traffic is automatically allowed.
- Network ACL (NACL) – Police Checkpoint at Neighborhood Entrance
- NACL = police checkpoint at the entrance of the neighborhood (subnet).
- Inspects everyone going in/out.
- Rules are stateless: if inbound is allowed, outbound must be explicitly allowed too.
- VPC Flow Logs – Surveillance Cameras
- Flow Logs = traffic cameras installed in the city.
- Record who goes where, and whether it succeeded or was blocked.
- Useful for troubleshooting (traffic jam, illegal intrusion).
- VPC Peering – Bridge Between Two Cities
- Peering = a bridge connecting two cities.
- Citizens can travel directly between them.
- But only two cities at a time → no central transit (no “hub and spoke”).
- Transit Gateway – Central Bus Station
- Transit Gateway = the central bus station.
- All cities connect here; to go anywhere, citizens pass through this hub.
- Centralized management, no need to build separate bridges for each pair.
- VPN Site-to-Site – Secret Tunnel
- VPN = a secret tunnel between CloudCity and your real-world city (on-premises).
- Protected by encryption (IPSec).
- Citizens can travel safely through this tunnel.
- AWS Direct Connect – Private Highway
- Direct Connect = a private high-speed highway from your company’s headquarters to CloudCity.
- Does not go through the Internet.
- High speed, low latency, stable, no congestion.
- Ideal for enterprises needing large bandwidth and reliability.
- Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) – Traffic Roundabout
- ELB = a roundabout at an intersection.
- When cars (requests) arrive, the roundabout distributes them evenly across multiple roads (EC2 servers).
- If one road is broken, the roundabout automatically blocks it, preventing cars from entering.
2 Practice labs how to create VPC, EC2, subnets, route tables, security groups, and internet gateways:
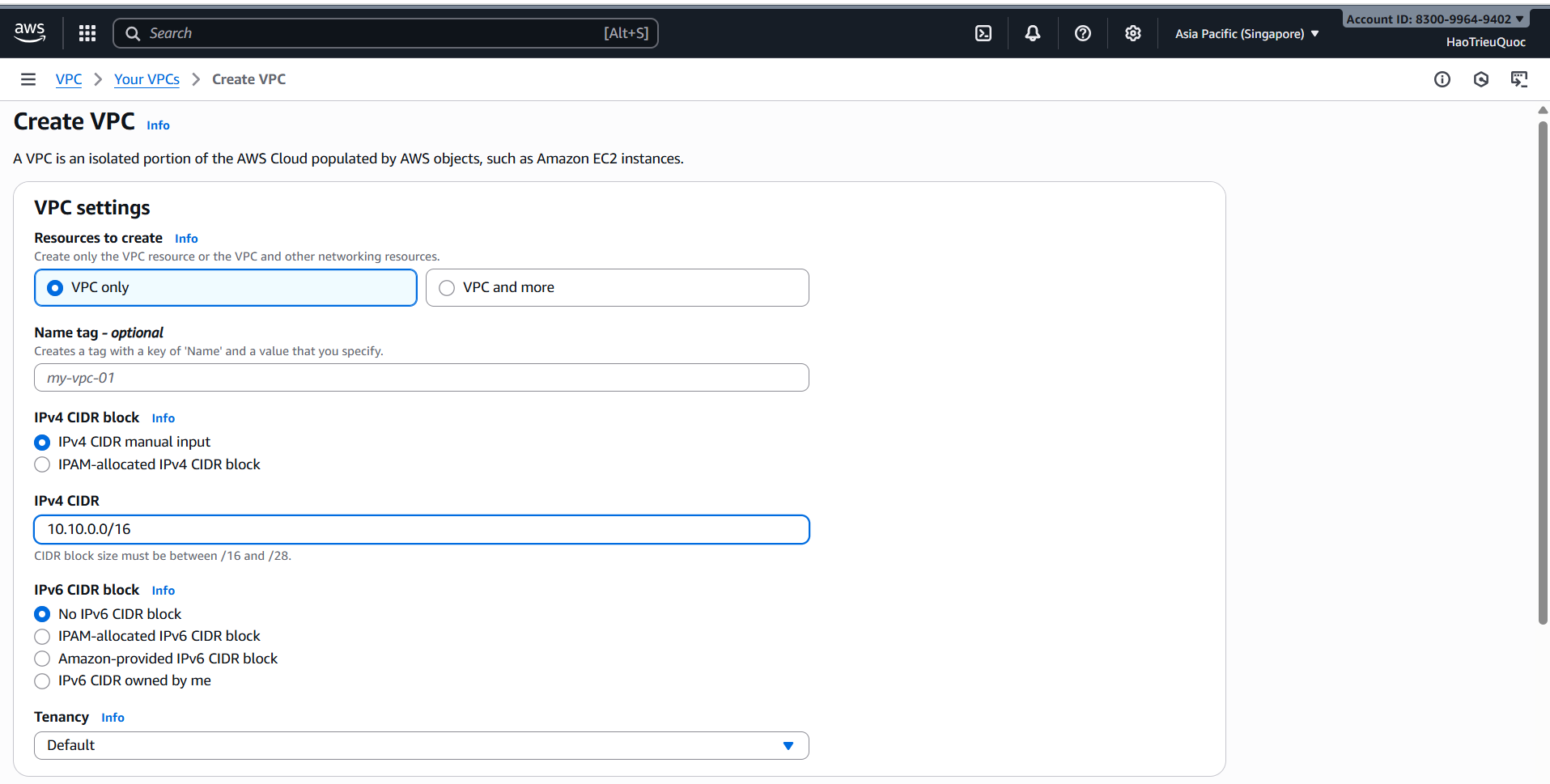
-Create VPC
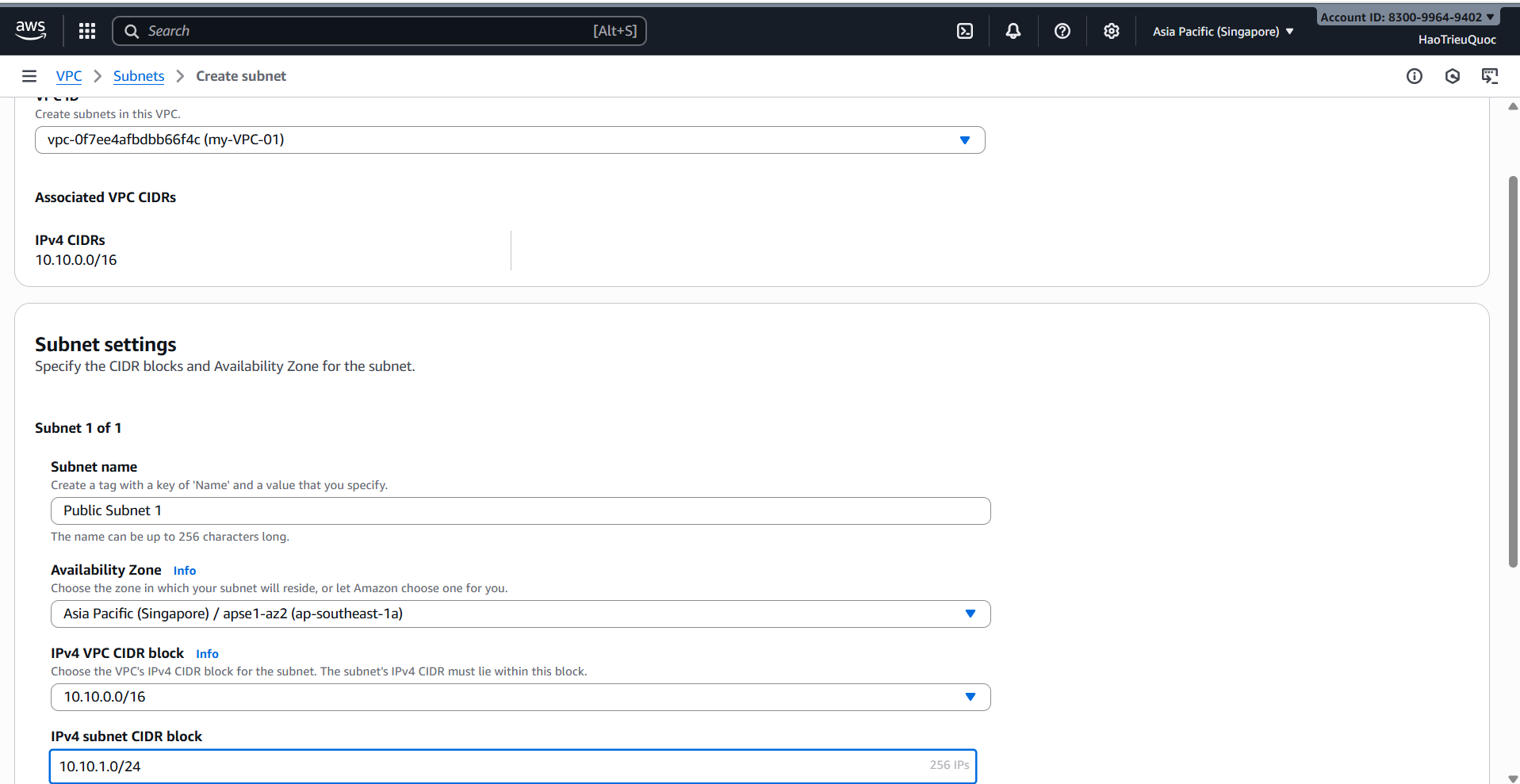
 -Create Subnet
-Create Subnet
 -Create Internet Gateway
-Create Internet Gateway
 -Create Route Table
-Create Route Table
 -Create Sercurity Groups
-Create Sercurity Groups
 -Create EC2
-Create EC2
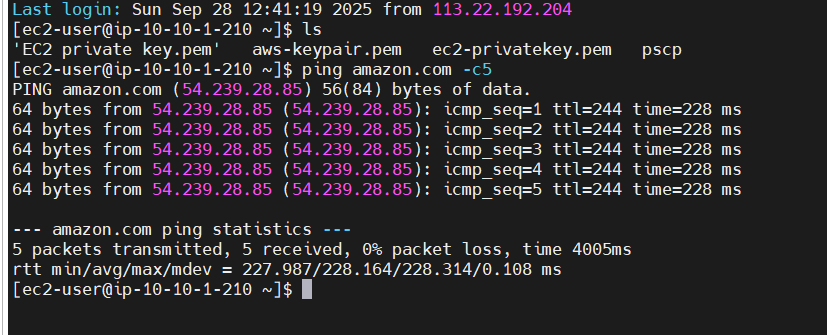
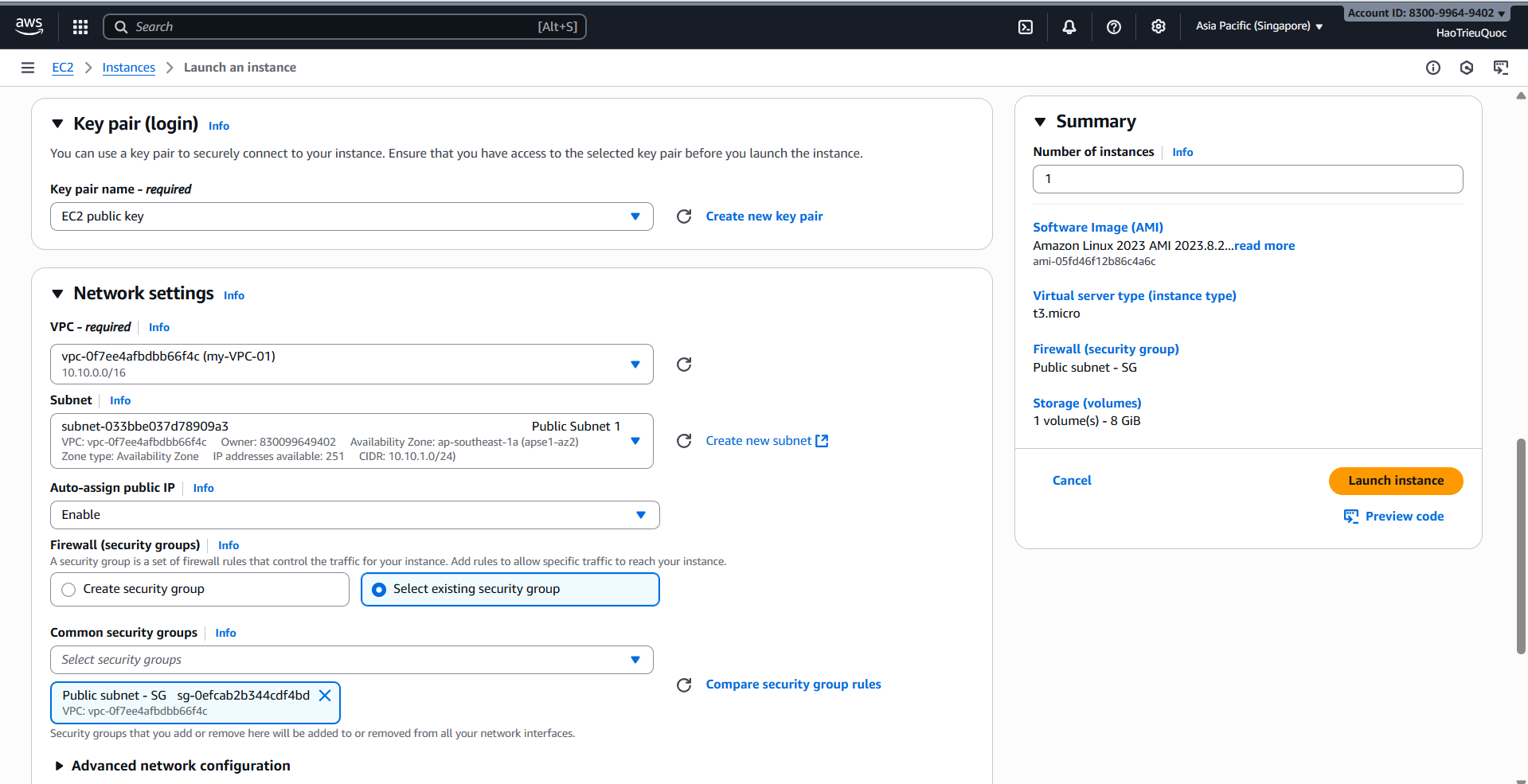 -Test Connection EC2
-Test Connection EC2
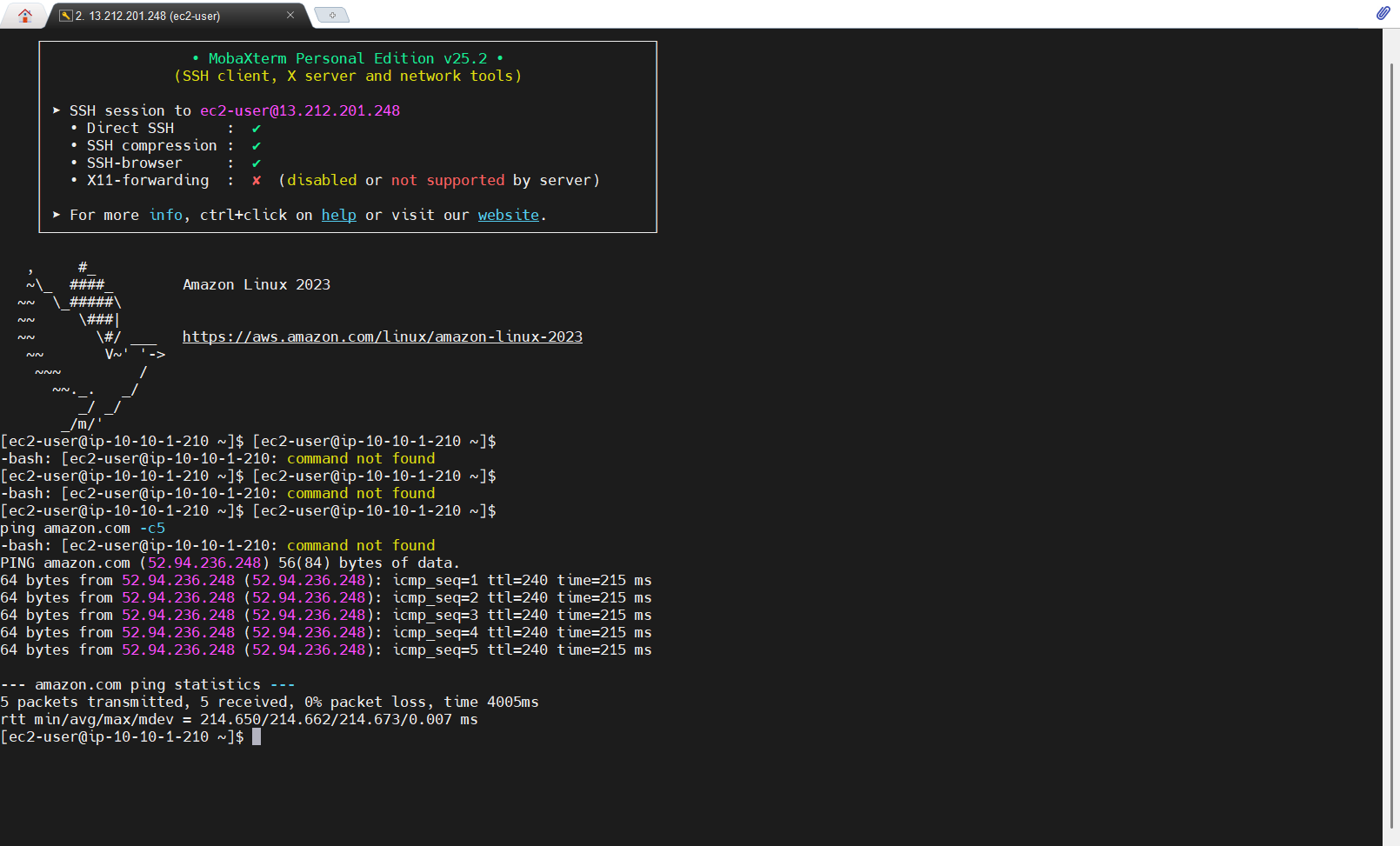 -Connection Private EC2
-Connection Private EC2
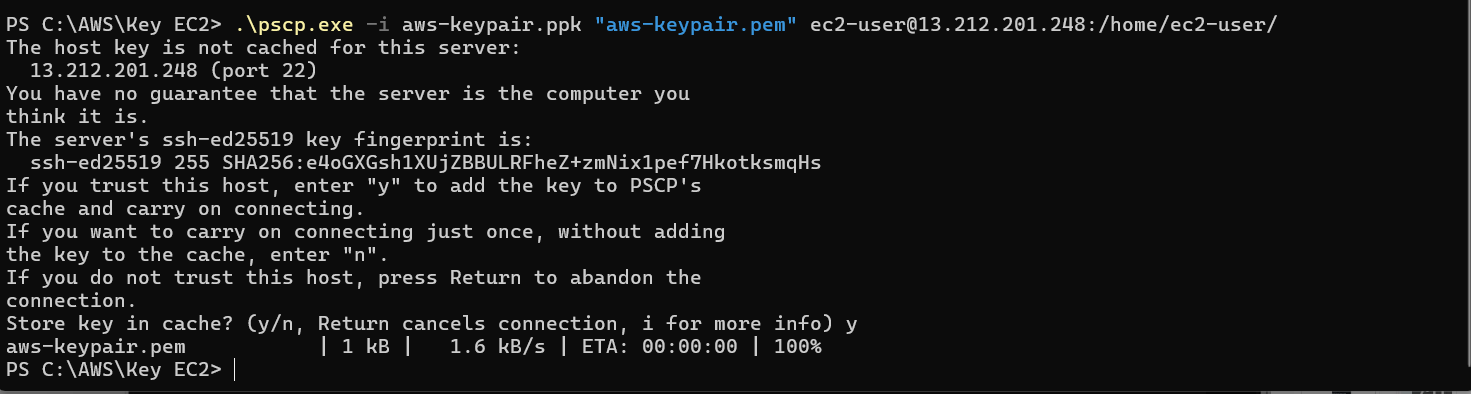
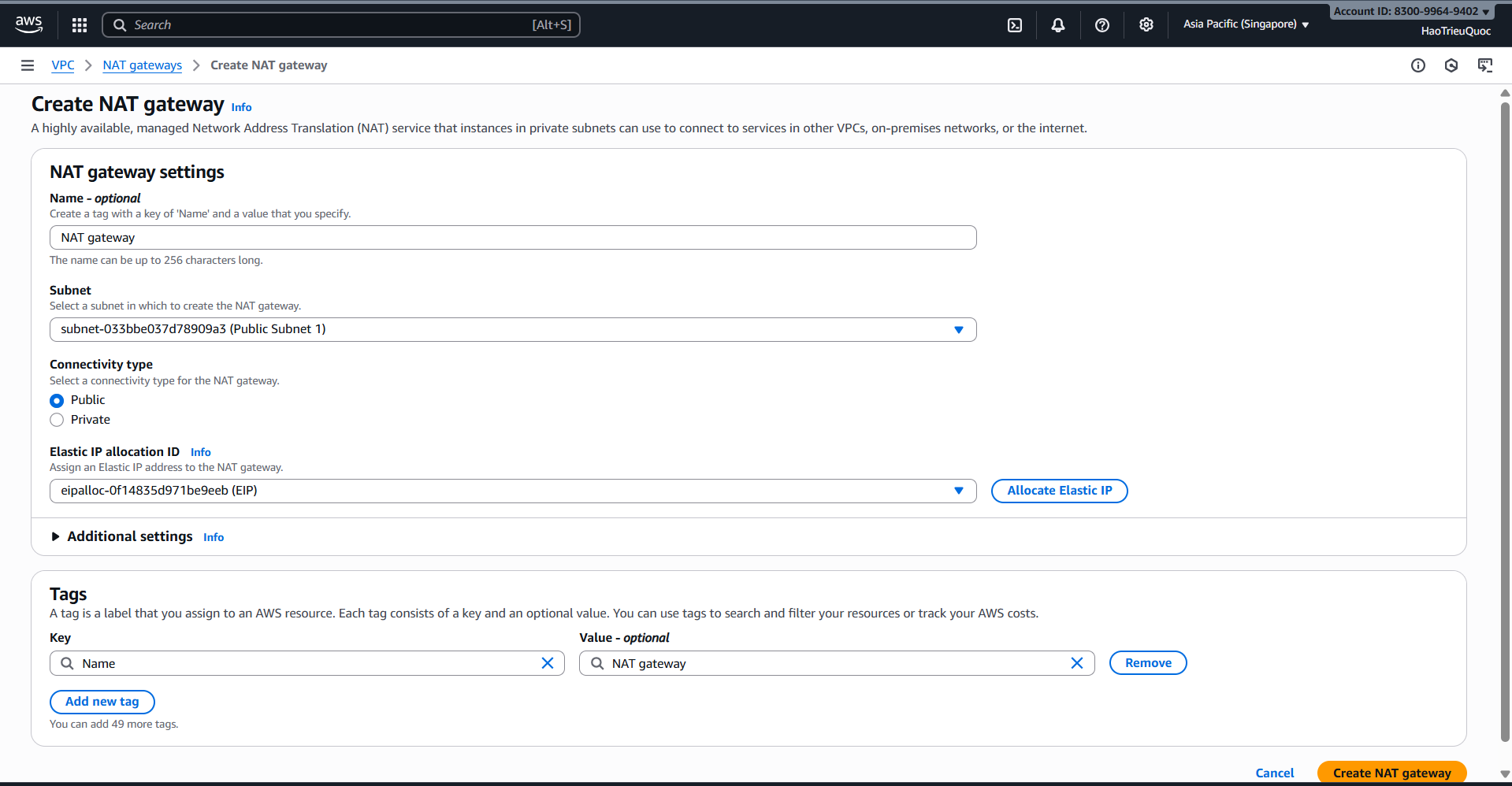
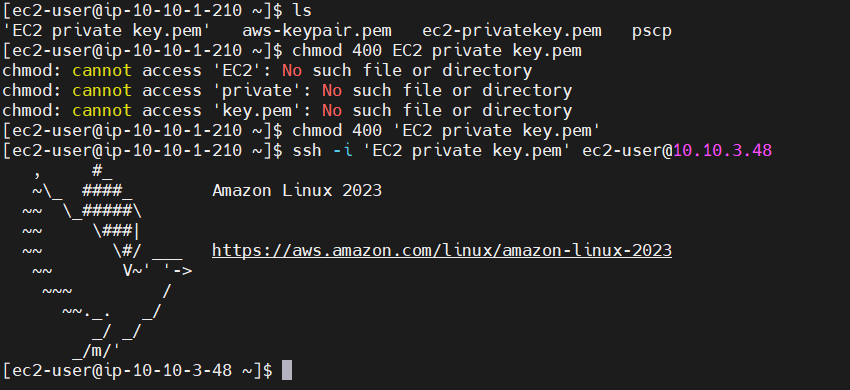 -Create NAT gateway
-Create NAT gateway