Week 4 Worklog
Week 4 Objectives:
- Learn fundamental AWS S3 concepts (storage, access control, data lifecycle).
- Understand how to configure S3 Buckets, Policies, ACLs.
- Explore S3 storage classes and performance optimization.
- Learn about disaster recovery, RTO, RPO, and AWS Backup.
Tasks to be carried out this week:
| Day | Task | Start Date | Completion Date | Reference Material |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - Study AWS S3 & Core Concepts: • Amazon S3 • S3 Bucket • Access point • Storage class • S3 Static website • S3 Control access • S3 ACL • S3 Bucket Policy • S3 Endpoint • Object Key & Performance | 09/29/2025 | 09/29/2025 | AWS Study Group |
| 2 | - Study Archival & Transfer Services: • Glacier • Snowball, Snowball Edge, Snowmobile | 09/30/2025 | 09/30/2025 | AWS Study Group |
| 3 | - Study Disaster Recovery Concepts: • RTO • RPO • AWS Backup | 10/01/2025 | 10/01/2025 | AWS Study Group |
| 4 | - Practice Deploy AWS Backup to the System Labs: create S3 bucket, Deploy Infrastructure, Create Backup Plan, Set up notifications, Test Restore, Clean up resources | 10/02/2025 | 10/02/2025 | LAB |
| 5 | - Practice Lab 57 again: Create S3 bucket, load data, config and test website | 10/03/2025 | 10/03/2025 | LAB |
Week 4 Achievements
1 Studied Amazon S3 & Core Concepts
- Amazon S3 – The Infinite Warehouse
- Concept: S3 is an object storage service for storing unlimited amounts of data.
- How it works: Stores data as objects (file + metadata) inside buckets.
- Example: Like Google Drive for developers, scalable to petabytes.
- S3 Bucket – The Container
- Concept: A container where objects are stored.
- How it works: Each bucket has a globally unique name, region, and policies.
- Example: Like a folder on your computer, but in the cloud.
- Access Point – Guest Door
- Concept: A simplified entry point to access S3 buckets.
- How it works: Each access point has its own hostname and permissions.
- Example: Like giving a guest a separate door key to your warehouse.
- Storage Class – Types of Shelves
- Concept: Defines durability, availability, and cost of storage.
- How it works: Options include Standard, Intelligent-Tiering, One Zone-IA, Glacier, etc.
- Example: Like choosing to store items in your bedroom (fast), basement (cheaper), or warehouse (cheap but far).
- S3 Static Website – Public Exhibition
- Concept: Hosting static websites directly from S3.
- How it works: Upload HTML/CSS/JS files, enable hosting, and access via URL.
- Example: Like pinning posters on a public board for everyone to see.
- S3 Control Access – Who Has the Keys
- Concept: Methods to control who can access data.
- How it works: Controlled by IAM policies, bucket policies, ACLs, and access points.
- Example: Like deciding which family members get house keys.
- S3 Access Control List (ACL) – Guest List
- Concept: Legacy method for managing access.
- How it works: Assigns read/write permissions to specific users.
- Example: Like making a guest list for a party with different access levels.
- S3 Bucket Policy – House Rules
- Concept: JSON-based rules for buckets.
- How it works: Define who can access, what actions are allowed or denied.
- Example: Like writing rules on the front door: “Open from 9AM–5PM only.”
- S3 Endpoint – Private Road
- Concept: Private connection between VPC and S3.
- How it works: Access S3 without traversing the public internet.
- Example: Like building a secret underground road to the warehouse.
- Object Key & Performance – Filing System
- Concept: Each object is identified by a unique key.
- How it works: Key design affects performance; avoid sequential names.
- Example: Like labeling documents in a filing cabinet for faster search.
- Glacier – Deep Freeze Storage
- Concept: Low-cost archival storage.
- How it works: Retrieval takes minutes to hours depending on request type.
- Example: Like putting old files in a frozen vault.
- Snowball, Snowball Edge, Snowmobile – Data Trucks
- Concept: Physical devices to transfer huge amounts of data.
- How it works:
- Snowball: suitcase-sized, TB scale.
- Snowball Edge: with compute/storage for edge processing.
- Snowmobile: truck-sized, exabyte scale.
- Example: Like shipping entire hard drives by truck instead of uploading.
- Disaster Recovery – Backup Plan
- Concept: Strategies to restore systems after outages.
- How it works: Uses backups, replication, and multi-region deployment.
- Example: Like having a fire escape plan for your house.
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO) – Downtime Tolerance
- Concept: Maximum downtime allowed.
- How it works: Defines how quickly services must recover.
- Example: Like promising to reopen a shop within 2 hours after blackout.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO) – Data Loss Tolerance
- Concept: Maximum acceptable data loss.
- How it works: Defines the amount of data (in minutes/hours) you can lose.
- Example: Like saying you can afford to lose notes from the last 10 minutes.
- AWS Backup – Centralized Backup Service
- Concept: Fully managed service for automating AWS backups.
- How it works: Supports EBS, RDS, DynamoDB, EFS, etc. with backup policies.
- Example: Like hiring a service to automatically back up your house documents.
2. Practice labs
- Create S3 bucket
- Create Folder
- Load data
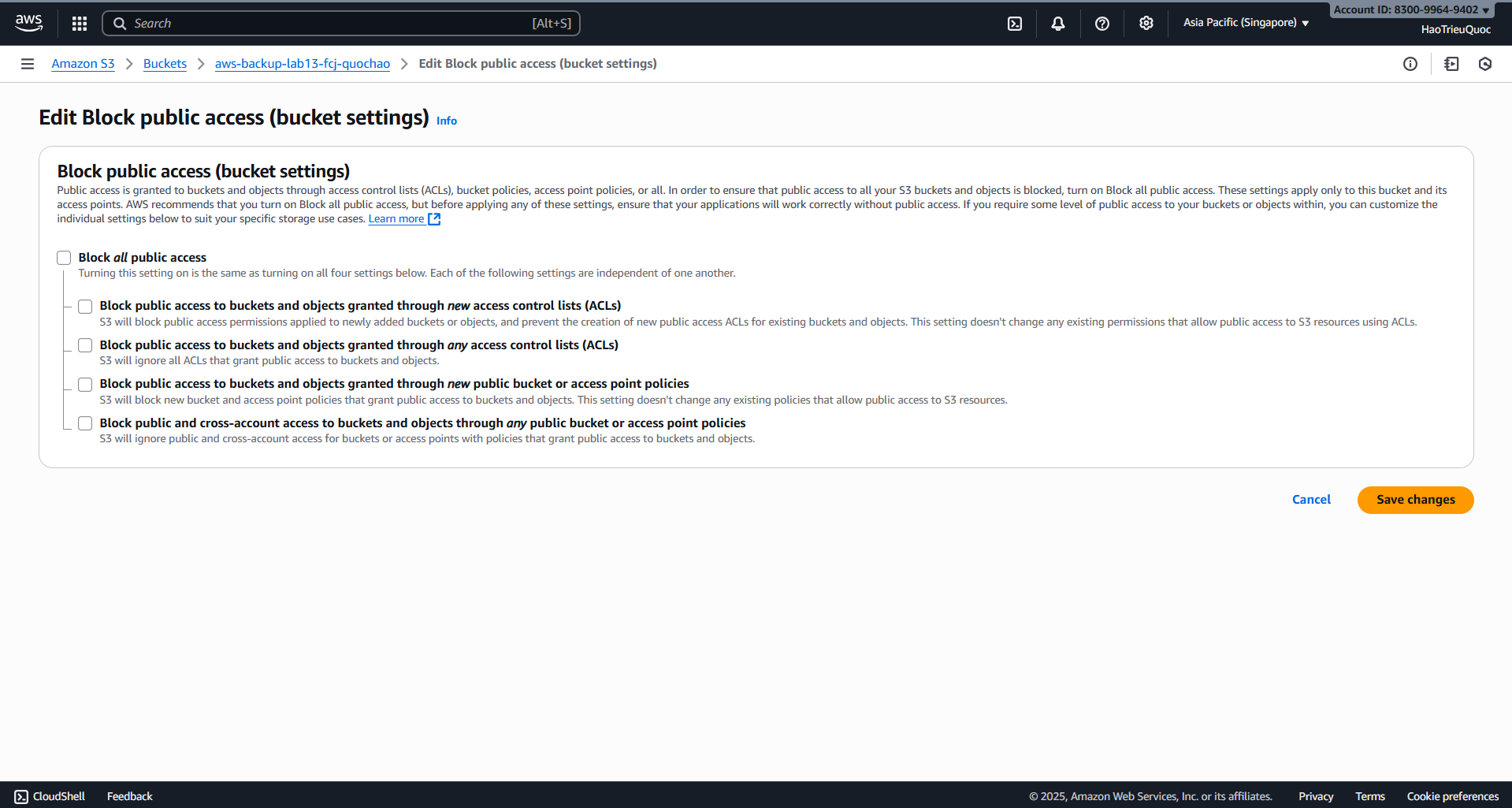
- Configuring public access block
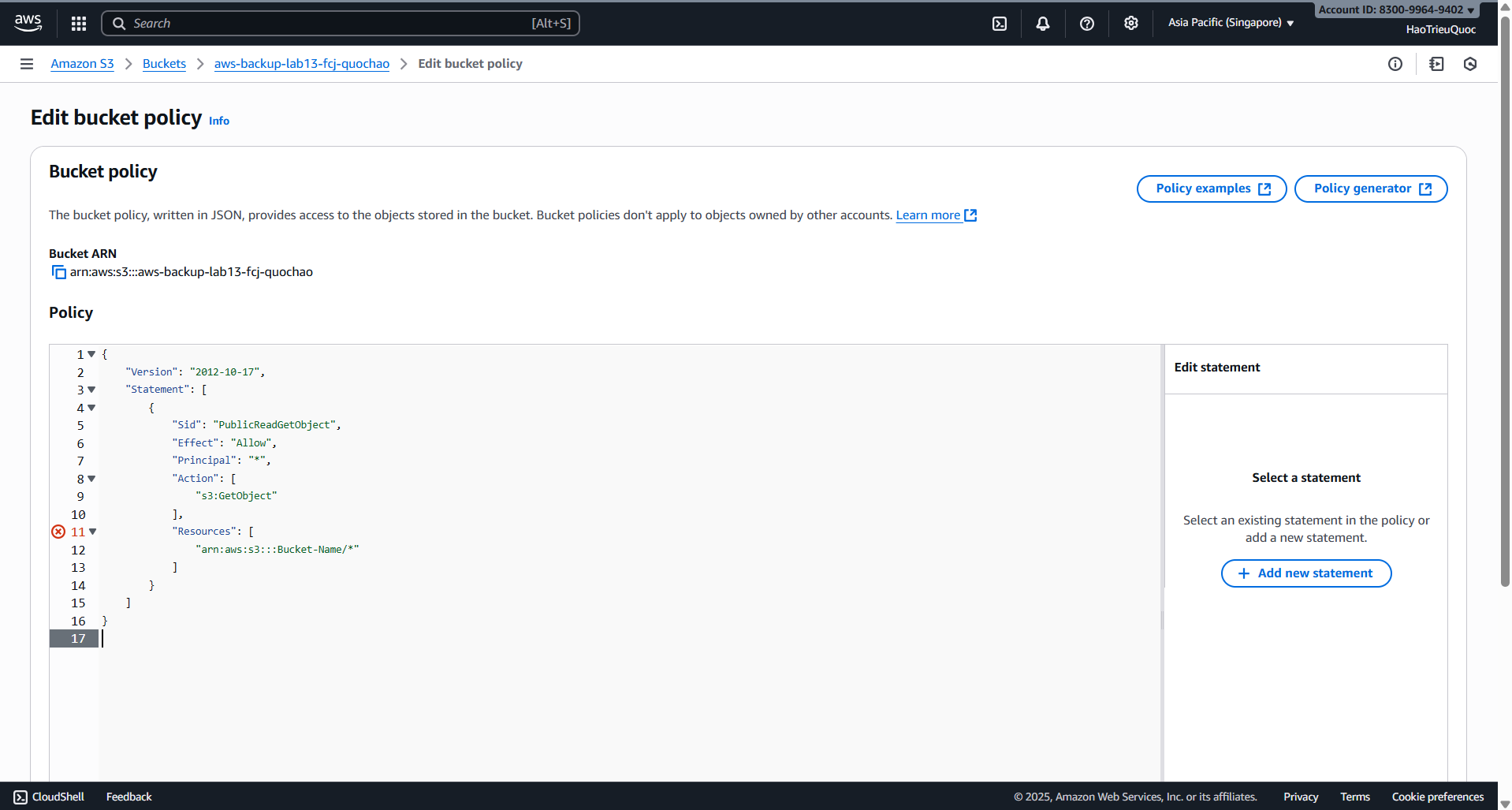
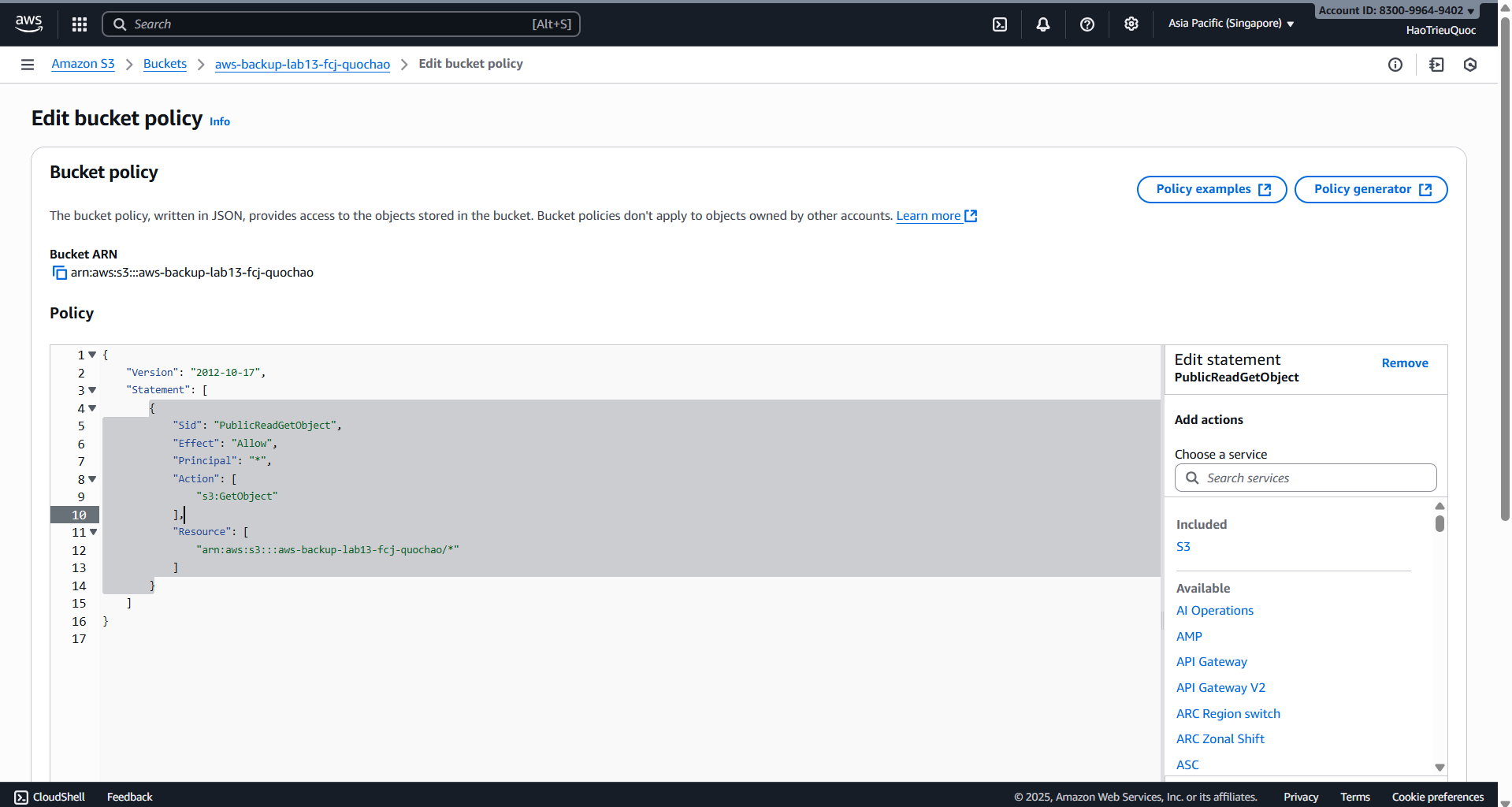
- Edit bucket policy
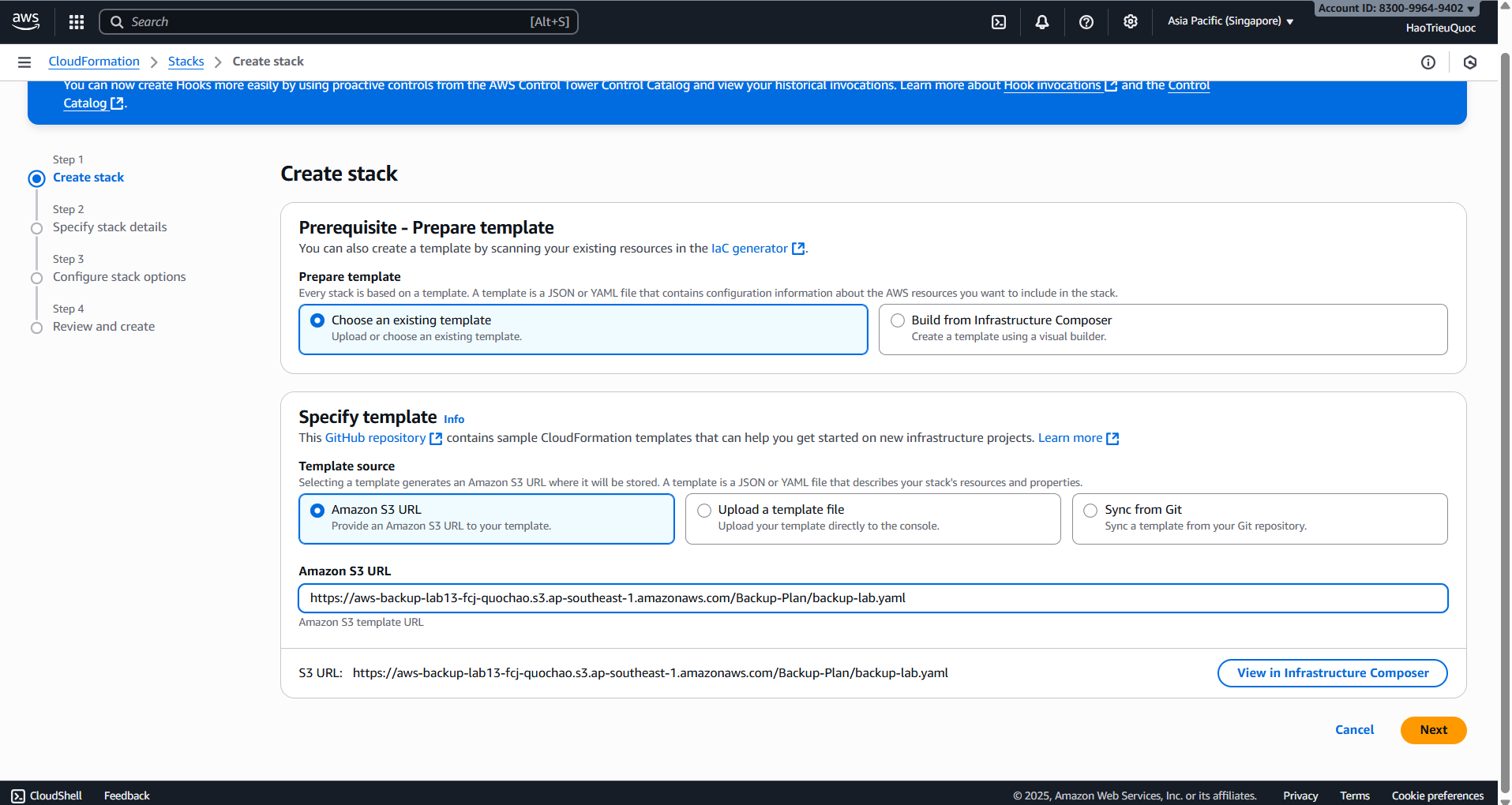
- Deploy Infrastructure
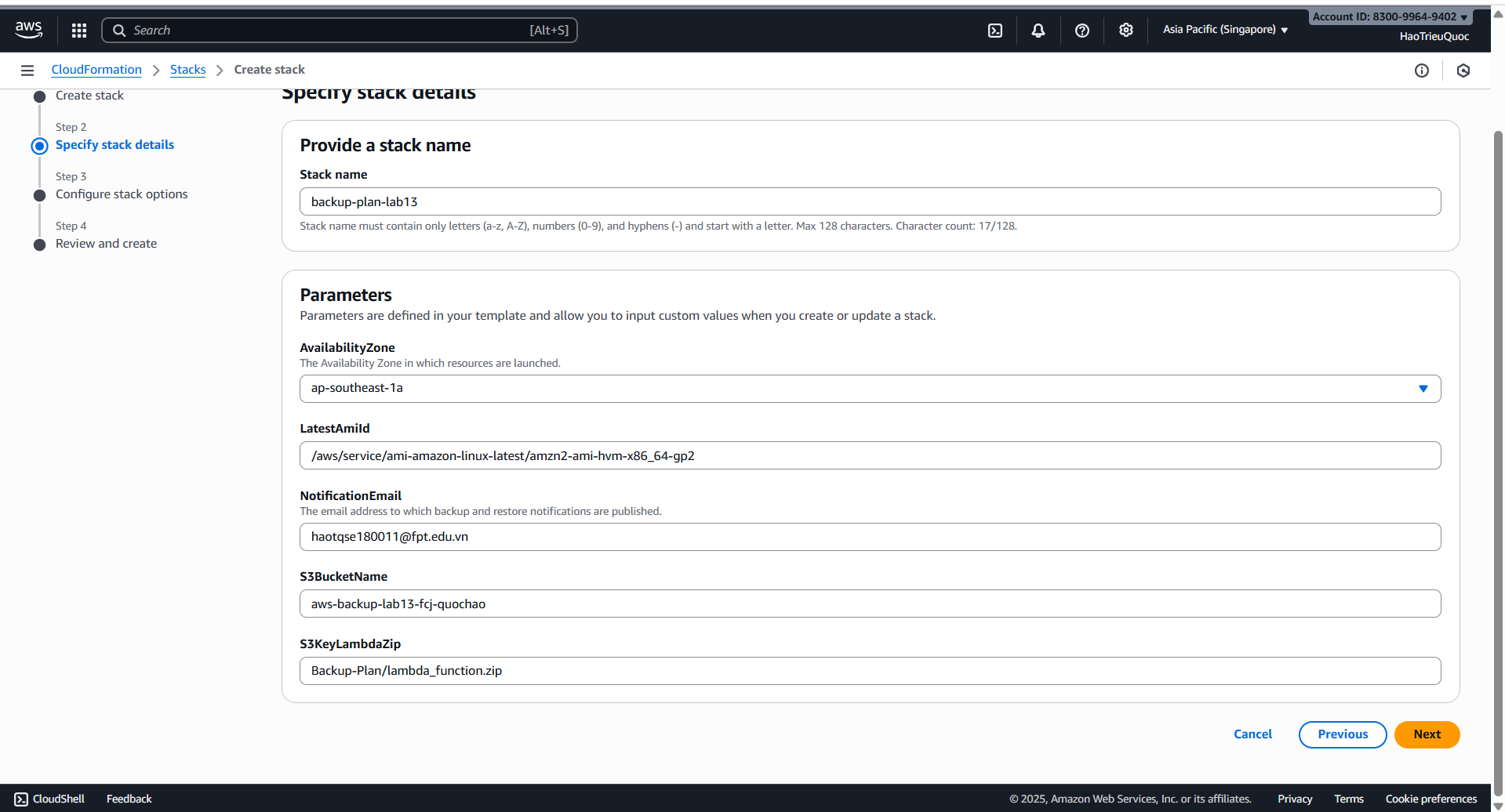
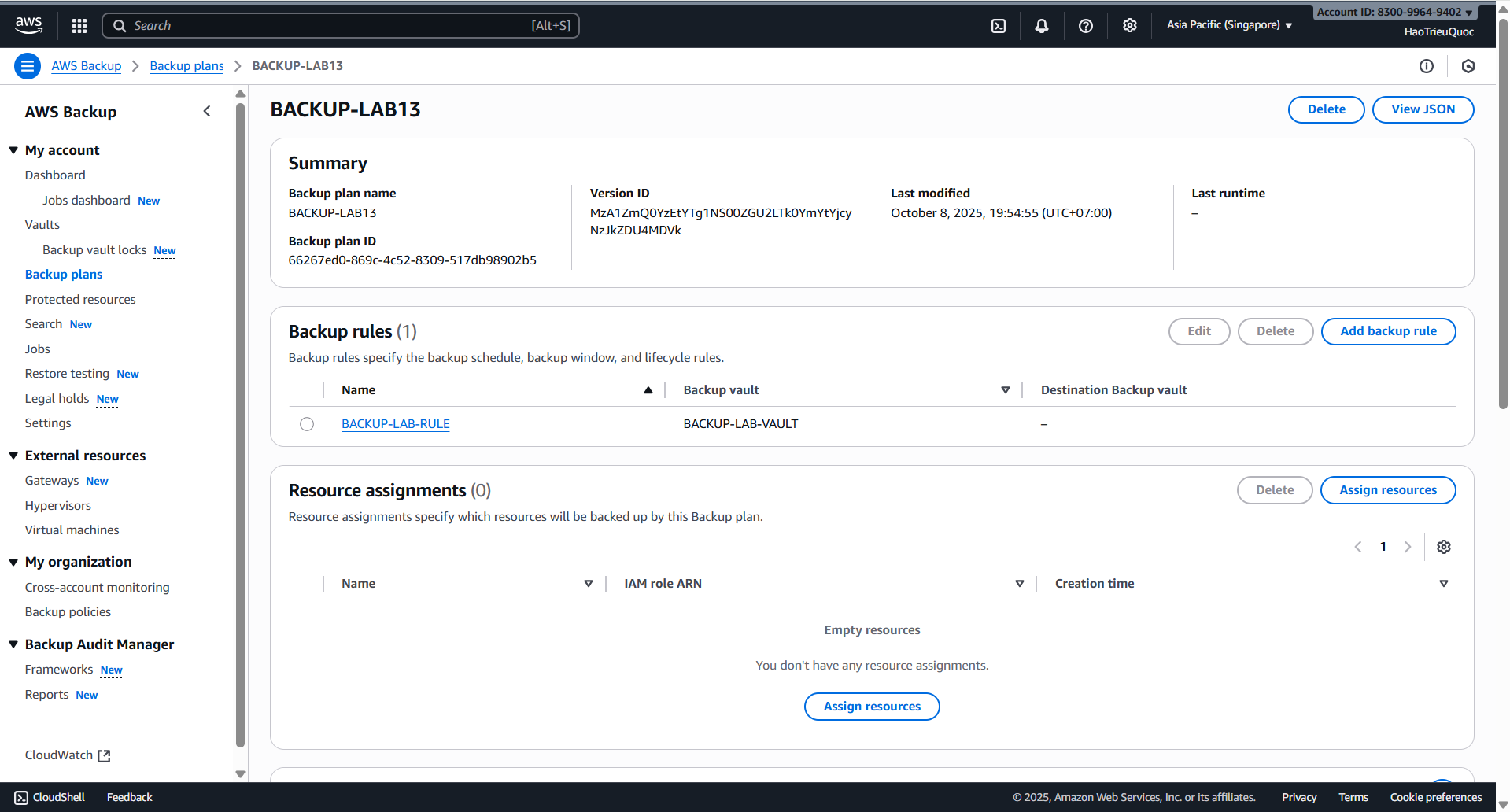
- Create backup plan
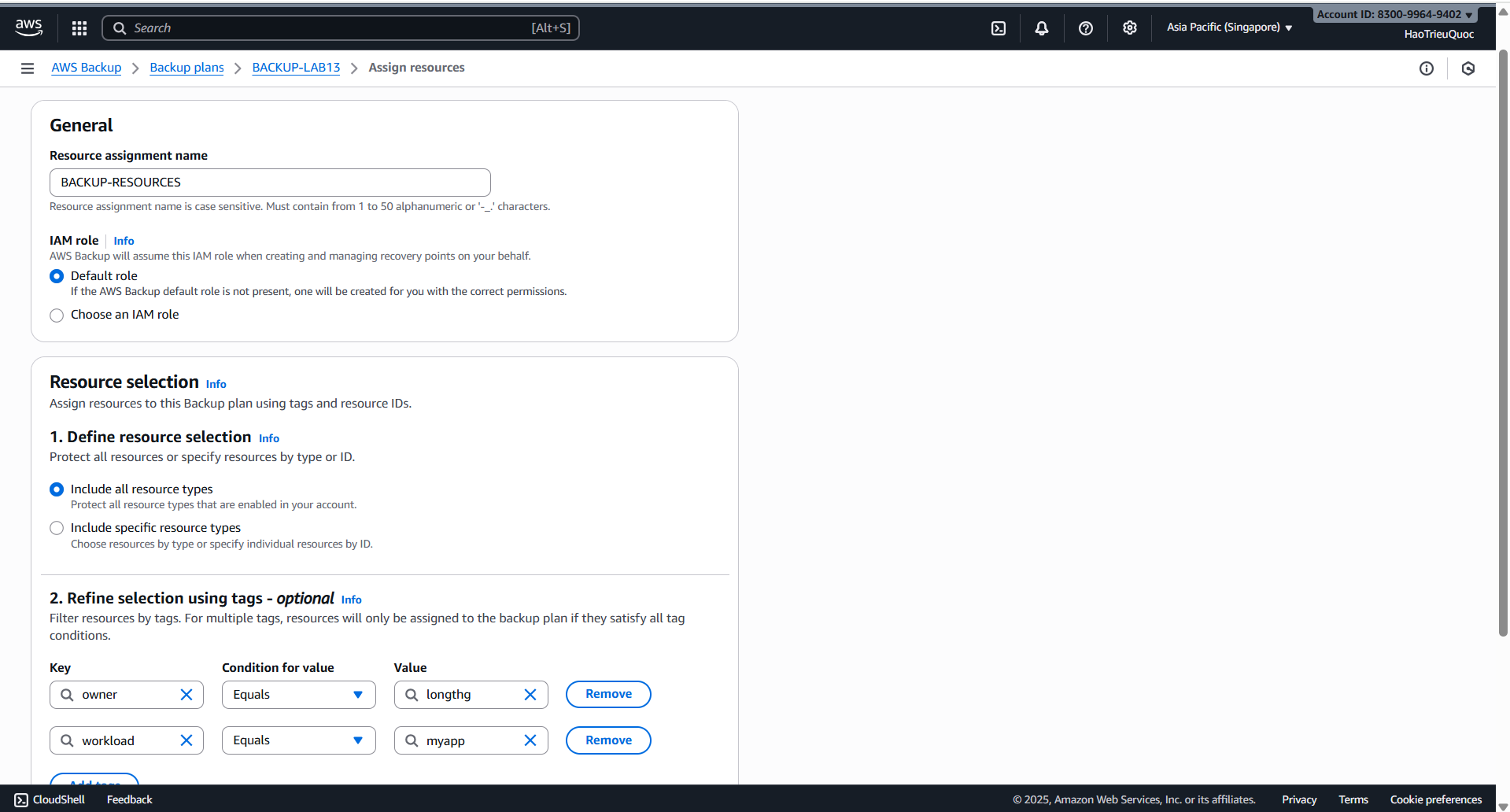
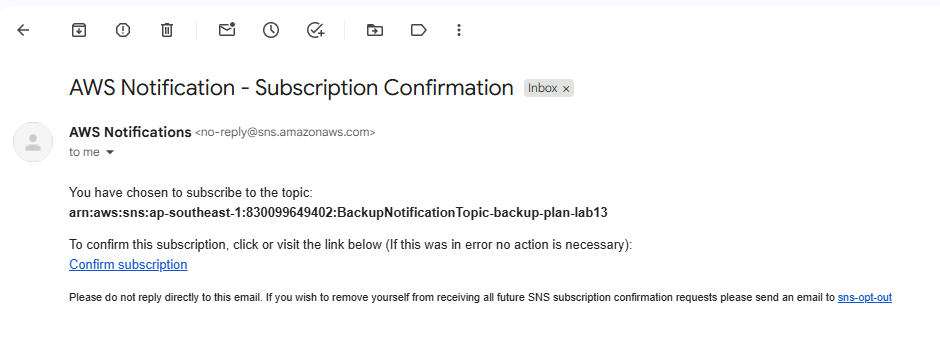
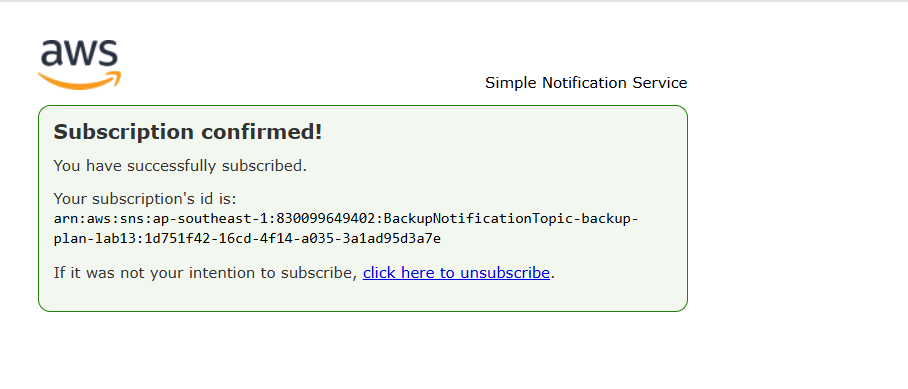
- Set up notifications
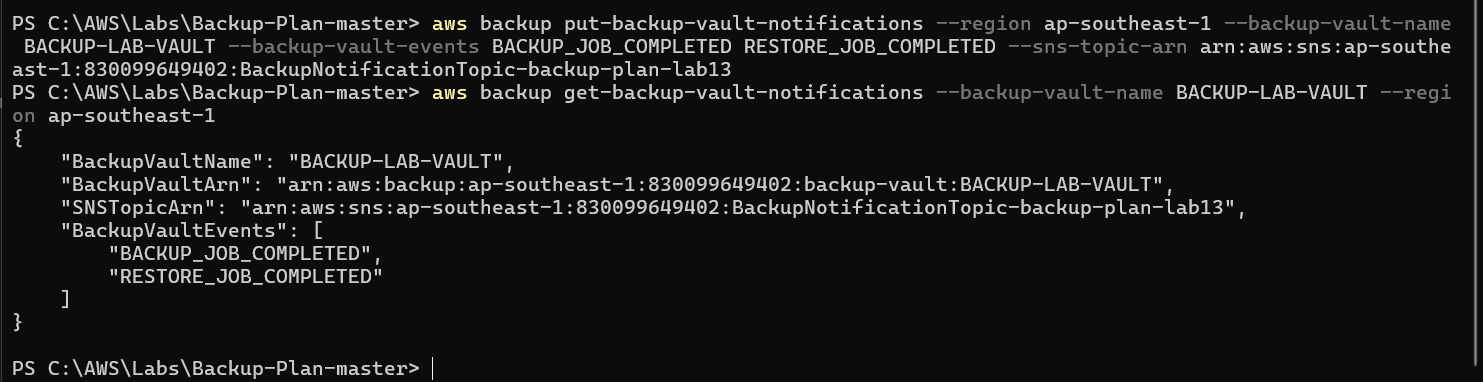
- Create on-demand backup
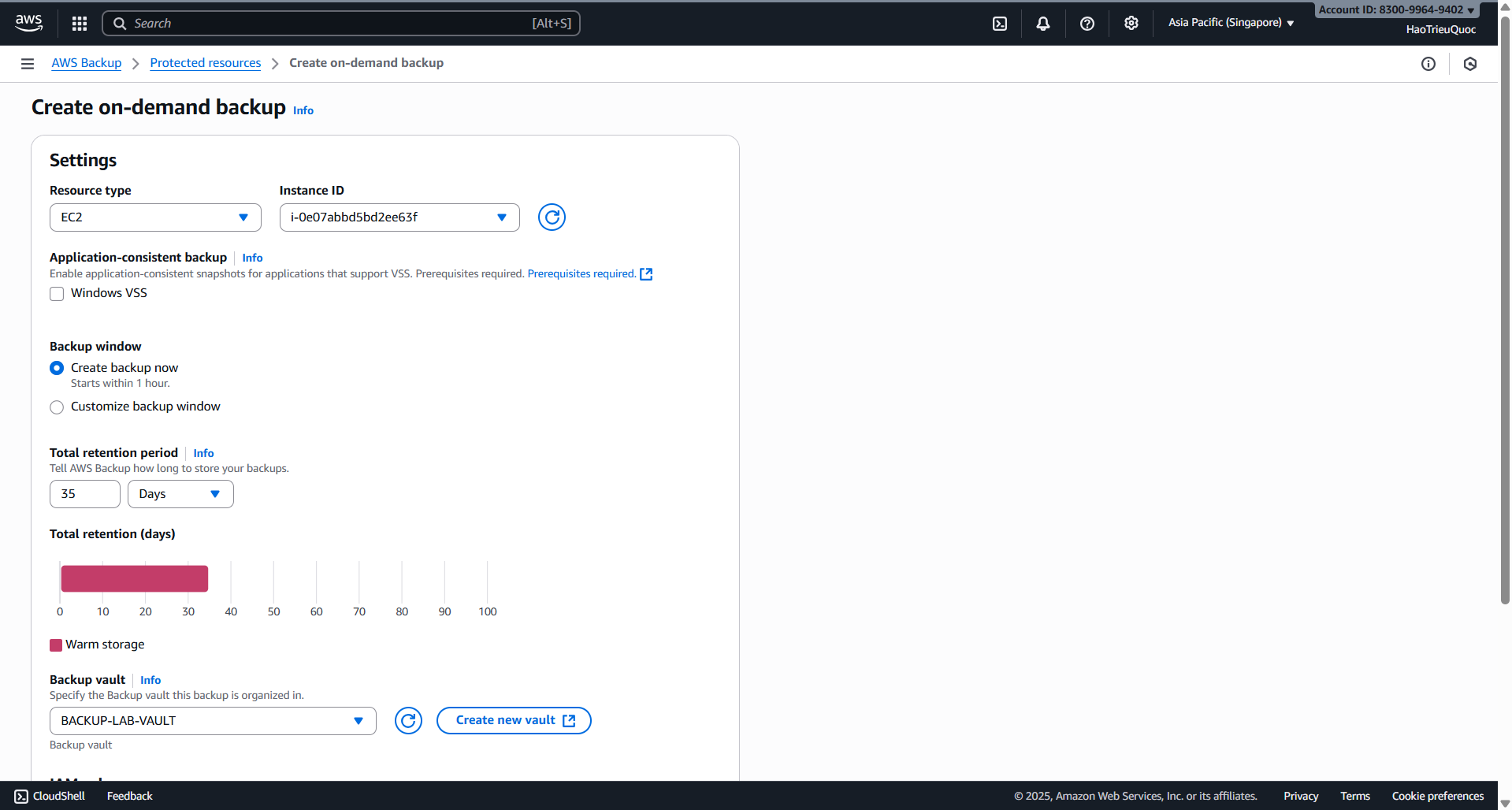
- Test restore
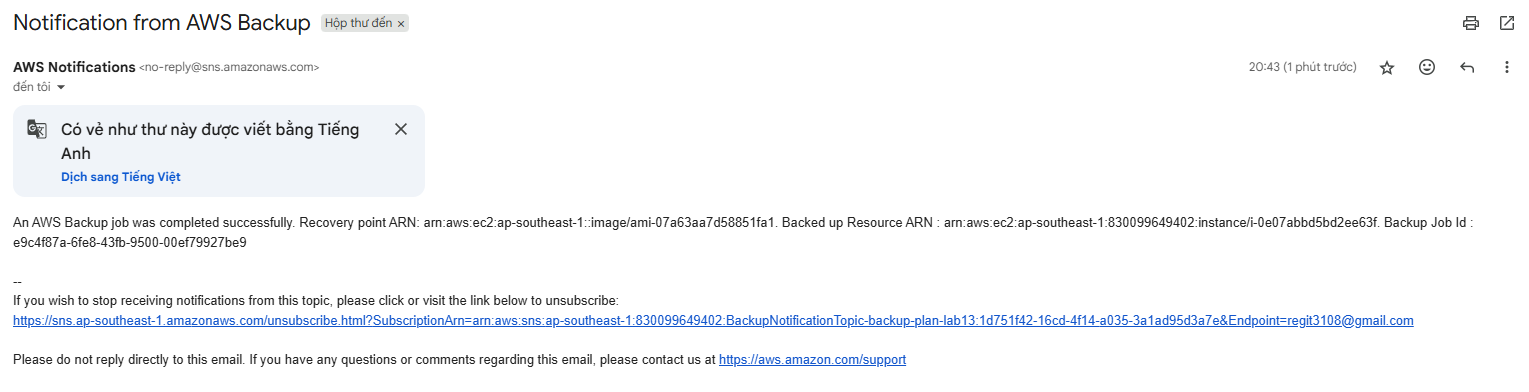
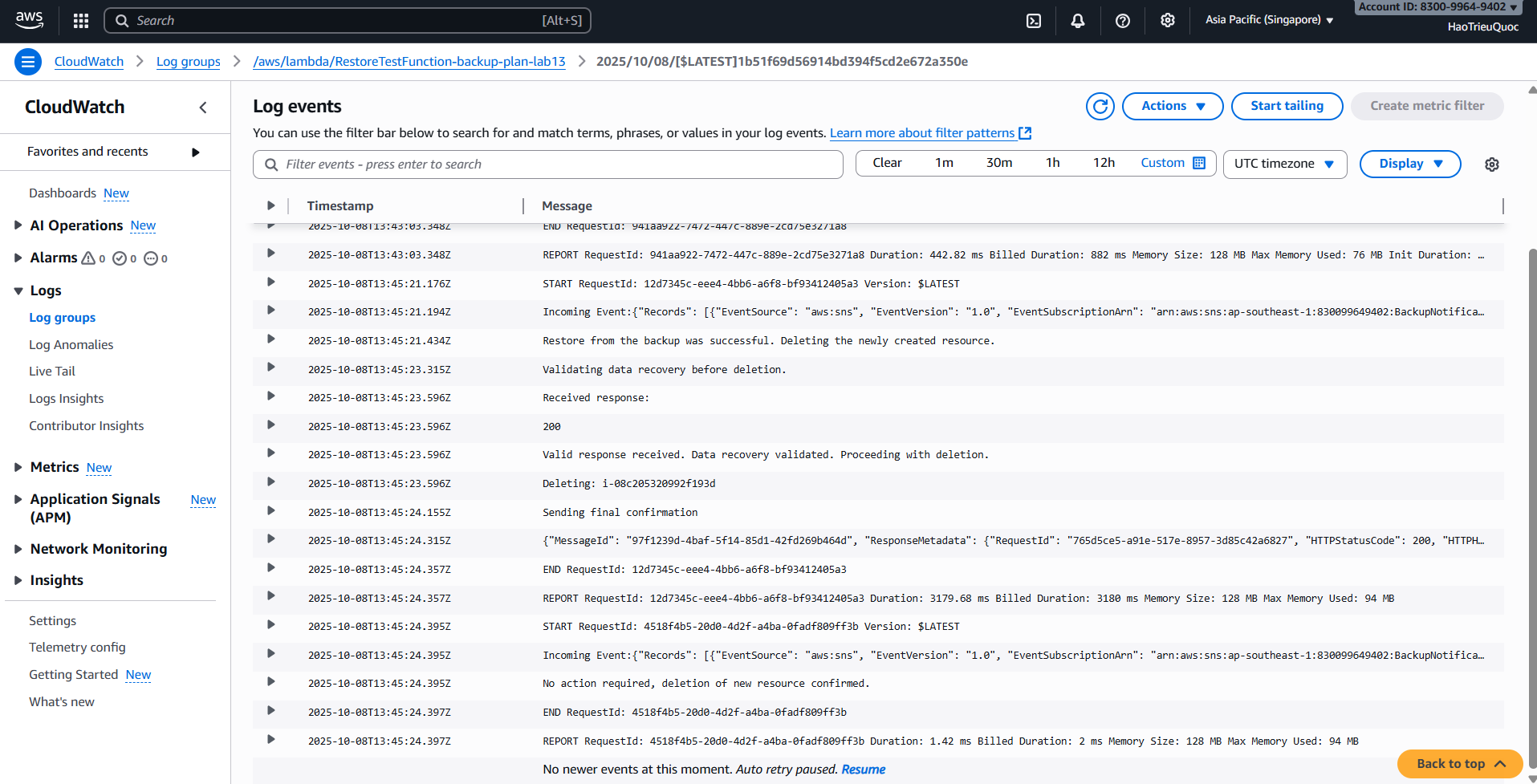
- Log stream
- Clean resources
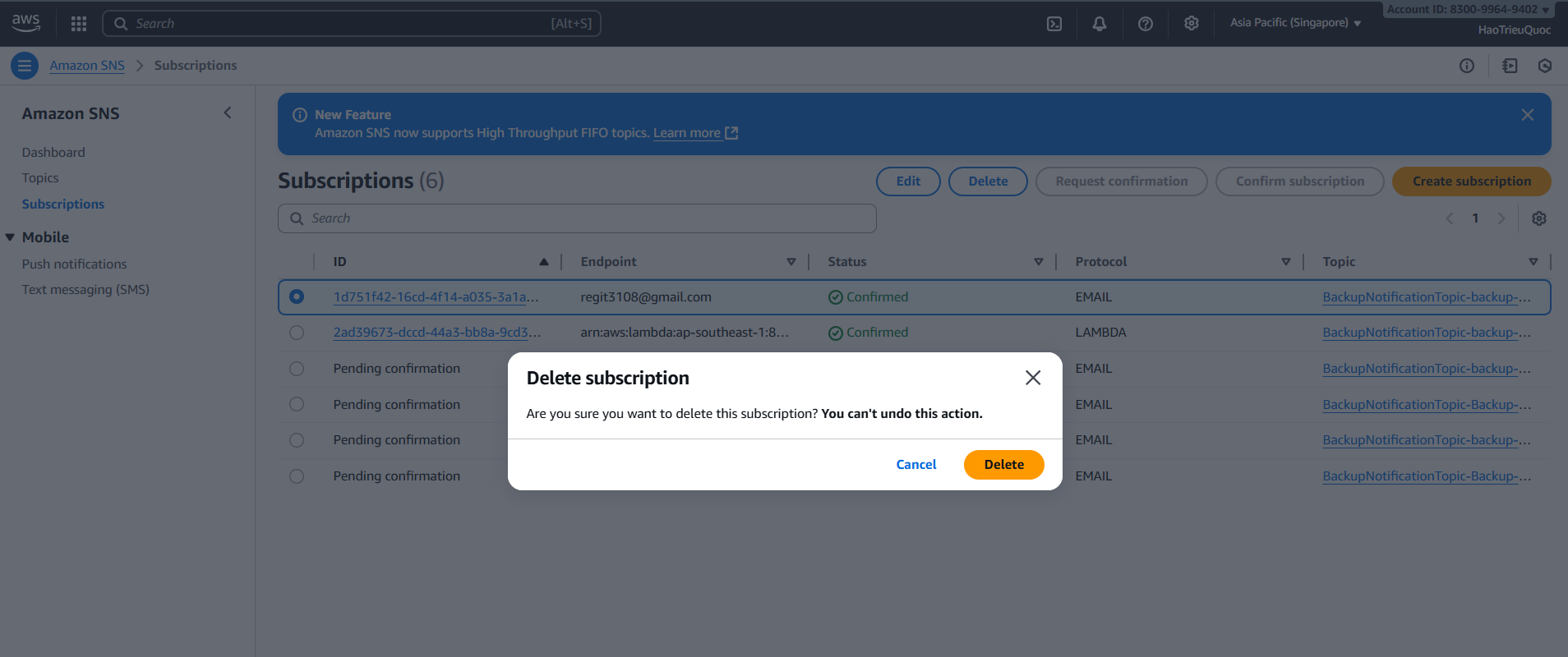
- Delete SNS
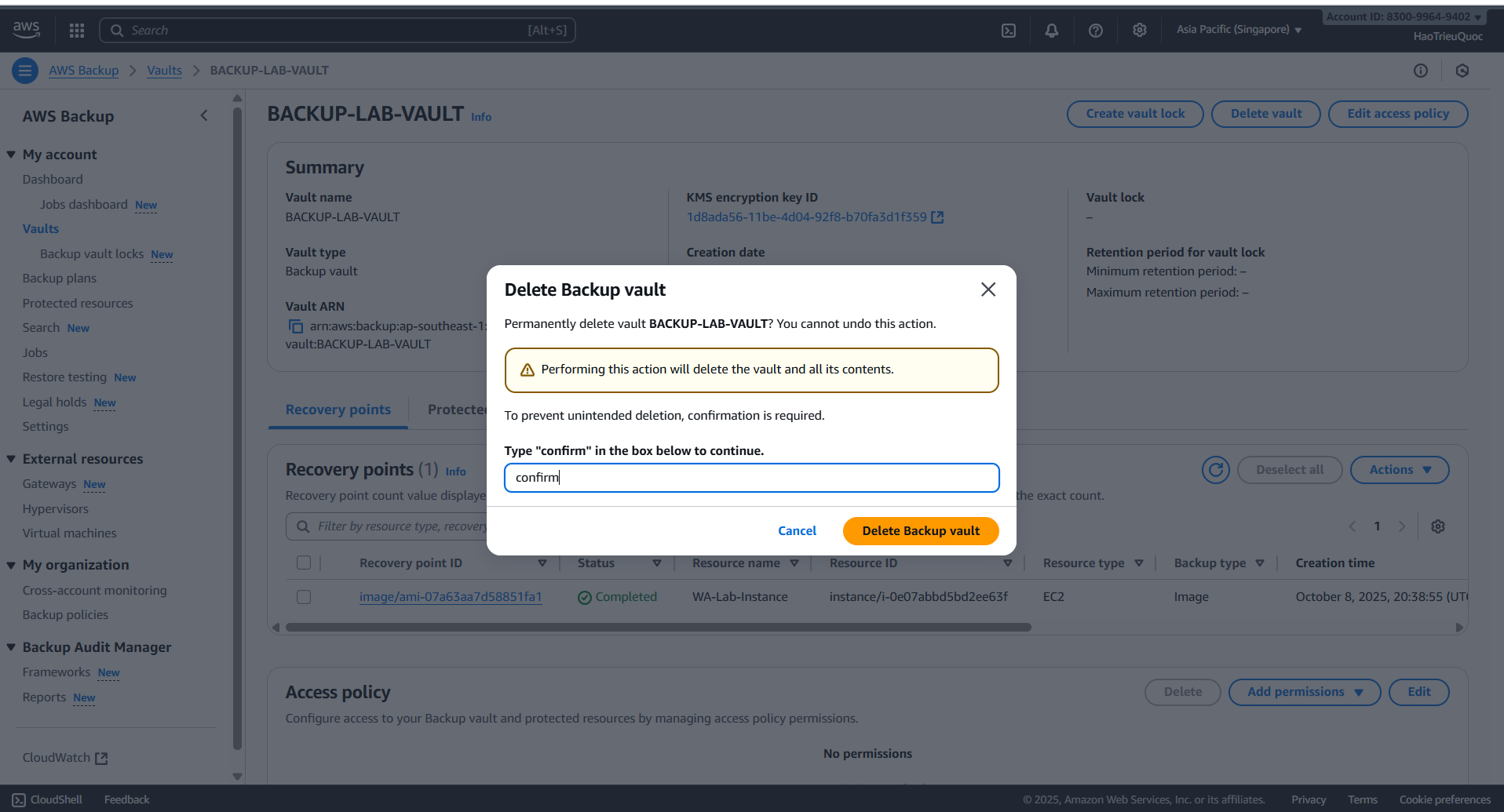
- Delete backup vault
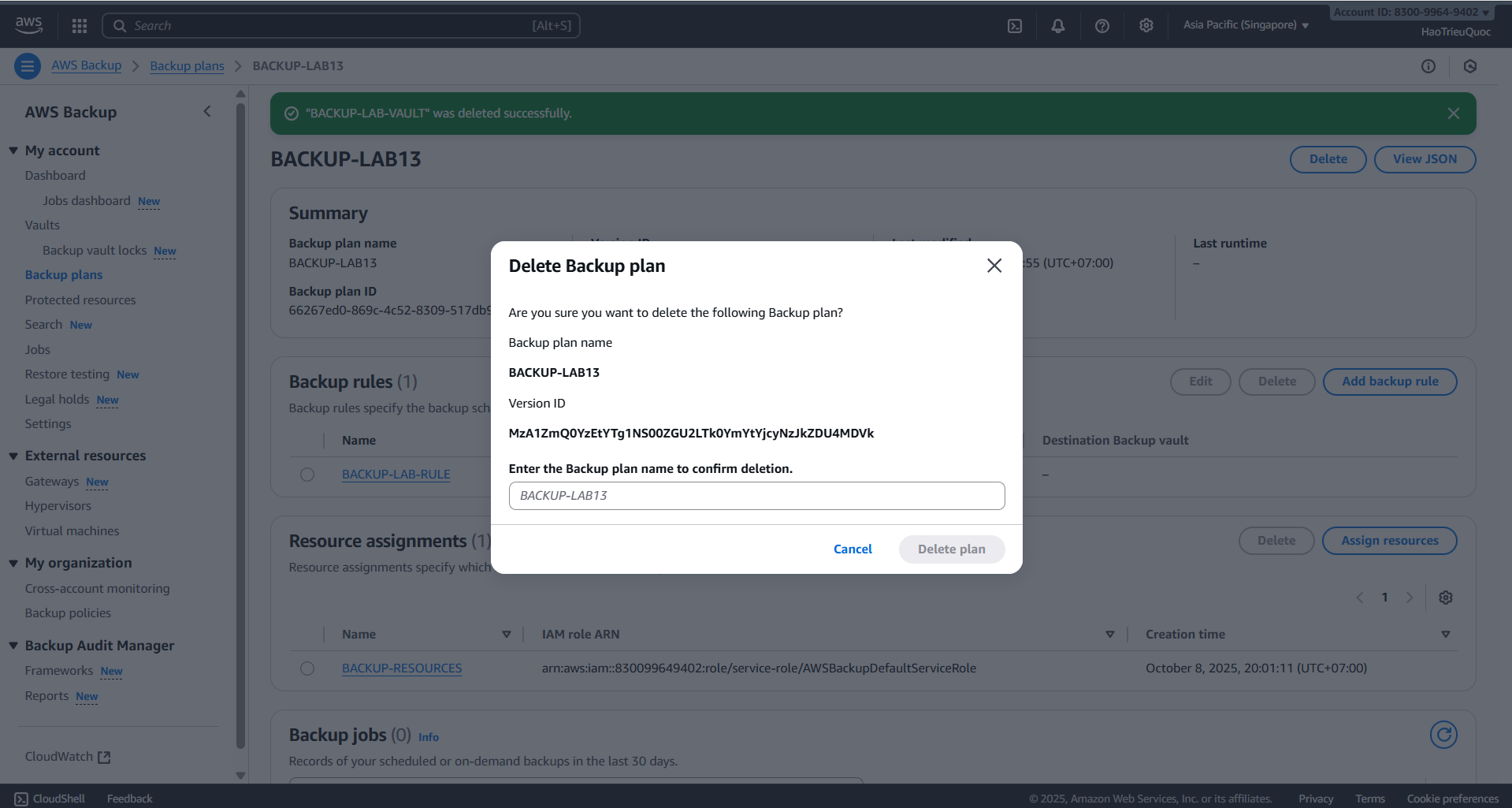
- Delete backup plan
- Delete Stacks
- Delete Log
- Terminate EC2