Week 5 Worklog
Week 5 Objectives:
- Understand the AWS Shared Responsibility Model and its division of responsibilities between AWS and customers.
- Learn about Identity and Access Management (IAM), Cognito, Organizations, and Identity Center (SSO) for centralized identity and access control.
- Explore AWS KMS (Key Management Service) and Security Hub for encryption and centralized security monitoring.
- Practice hands-on labs on IAM roles, user management, SSO integration, and security auditing.
- Project preparation: research Clickstreams, Sections, and Track 4 requirements in FCJ. Collaborate as a team to understand the project direction.
Tasks to be carried out this week:
| Day | Task | Start Date | Completion Date | Reference Material |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-2 | - Study AWS Security and Identity Concepts: • Shared Responsibility Model • AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) • Amazon Cognito • AWS Organization • AWS Identity Center (SSO) • AWS KMS • AWS Security Hub | 10/06/2025 | 10/07/2025 | AWS Study Group |
| 3-4 | - Practice IAM Labs: create IAM users, groups, roles, and policies; test permissions and MFA login | 10/08/2025 | 10/09/2025 | LAB |
| 5 | - Determine the group project topic: Batch-based Clickstream Analytics Platform. - Research what Clickstreams are and how they are used in analytics. - Learn about Sections in the project structure and how they relate to data collection and processing. - Study the requirements of Track 4 in the FCJ program to align the project objectives. - All team members collaborate to discuss and research the above topics together. | 10/10/2025 | 10/10/2025 |
Week 5 Achievements
1. AWS Security and Identity Management Concepts
- Shared Responsibility Model
Concept: AWS and customers share security responsibilities but in different scopes.
AWS is responsible for Security of the Cloud — securing physical infrastructure, hardware, networks, and data centers.
Customers are responsible for Security in the Cloud— protecting their data, managing user access, and configuring resources securely.How it works: AWS ensures the cloud environment is secure, while users must configure their own resources properly — for example, not making an S3 bucket public if it contains sensitive data.
Example: AWS is like a building owner who secures electricity, water, and fire systems.
You rent an apartment — you must lock your door and keep your belongings safe.
- AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Concept: A service that manages users, groups, and access permissions in AWS.
It’s the foundation of identity and permission management.How it works: -IAM User: an AWS account identity.
-IAM Group: a collection of users.
-IAM Role: temporary permissions for users or services.
-IAM Policy: JSON document defining allowed or denied actions.Example: IAM is like an office access control system.
Employees get ID cards (users) with specific door access (policies).
Guests get temporary badges (roles).
- Amazon Cognito
Concept: A service for authenticating and managing users for web or mobile applications.
Allows registration, login, and session management.How it works: -Create User Pools to manage identities.
-Supports login via email or social providers (Google, Facebook, Apple).
-After login, Cognito issues tokens to access AWS resources (like S3 or API Gateway).Example: Cognito is like a building’s reception desk — it verifies identity and gives access cards (tokens) to visit different rooms (services).
- AWS Organization
Concept: A service that manages multiple AWS accounts under one organization.
It allows centralized billing, policies, and permissions.How it works: -Create a root account, then add member accounts.
-Apply Service Control Policies (SCP) to set permission boundaries across the organization.Example: Like a parent corporation managing subsidiaries.
The head office defines common policies (SCP), while each branch operates independently but under supervision.
- AWS Identity Center (SSO)
Concept: Provides Single Sign-On (SSO) access to multiple AWS accounts and SaaS applications using one login.
How it works: -Integrates with AWS Organizations or external identity providers (Microsoft AD, Okta).
-Once users log in via Identity Center, they can access all authorized accounts and apps without re-entering credentials.Example: It’s like a multi-building employee access card — one scan grants entry to multiple offices in the company.
- AWS Key Management Service (KMS)
Concept: A service that manages encryption keys to protect data.
AWS helps create, rotate, and control key usage.How it works: -Create Customer Master Keys (CMK).
-Use CMKs to encrypt data in S3, EBS, RDS, etc.
-Only authorized IAM users can use keys.Example: KMS is like a central bank vault — you can deposit (encrypt) or withdraw (decrypt) only with the correct key (permissions).
- AWS Security Hub
Concept: A centralized security service that aggregates, analyzes, and evaluates findings from multiple AWS security tools.
It gathers data from services like GuardDuty, Inspector, and Macie into one security dashboard.How it works: -Security Hub scans all accounts to identify vulnerabilities (findings).
-It provides compliance scores based on frameworks like CIS AWS Foundations Benchmark.Example: It’s like a smart building’s central security panel — collecting alerts from cameras, fire alarms, and sensors, allowing security teams to monitor everything from one place.
2. Practice labs
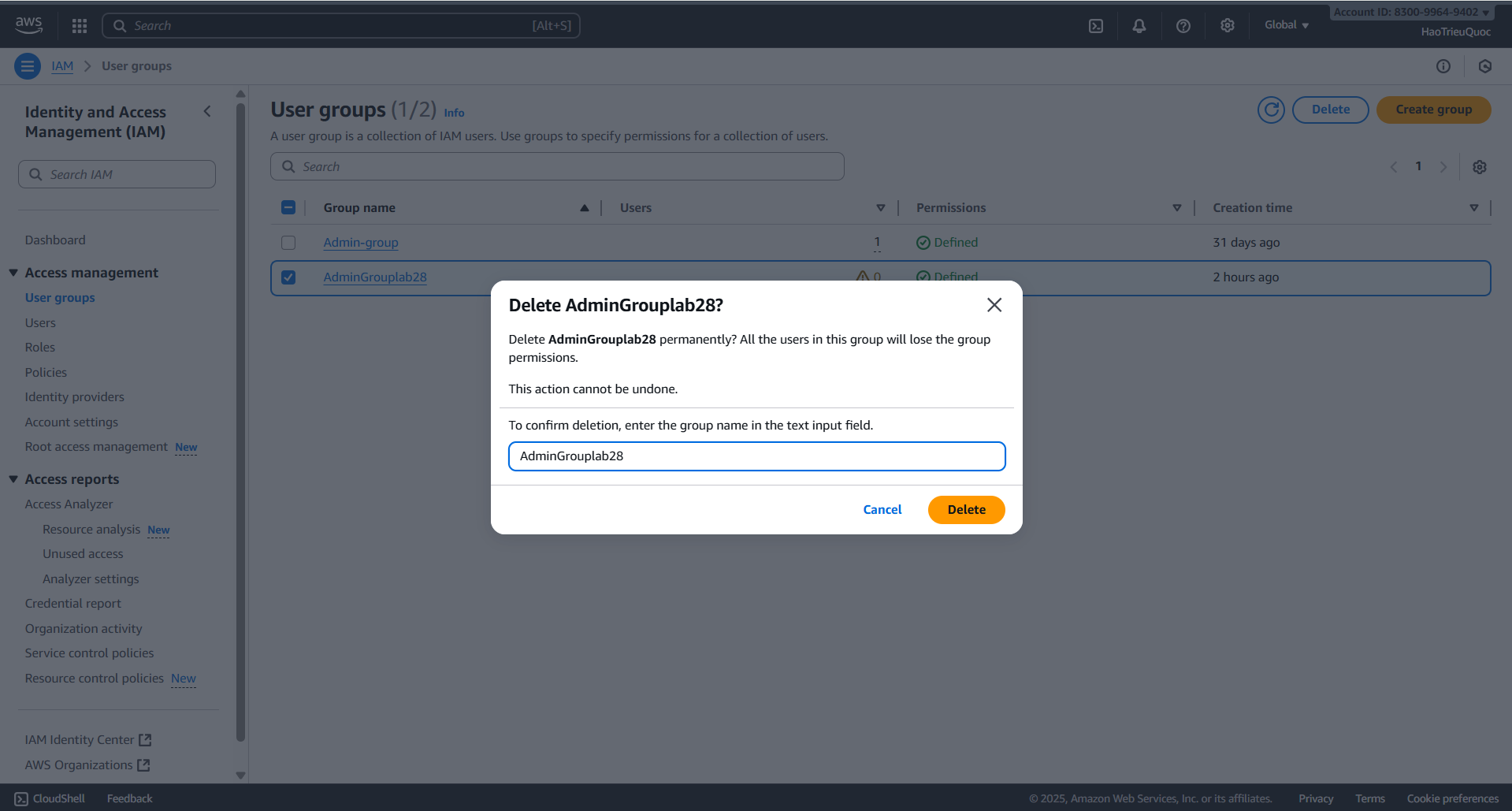
- Create User Group
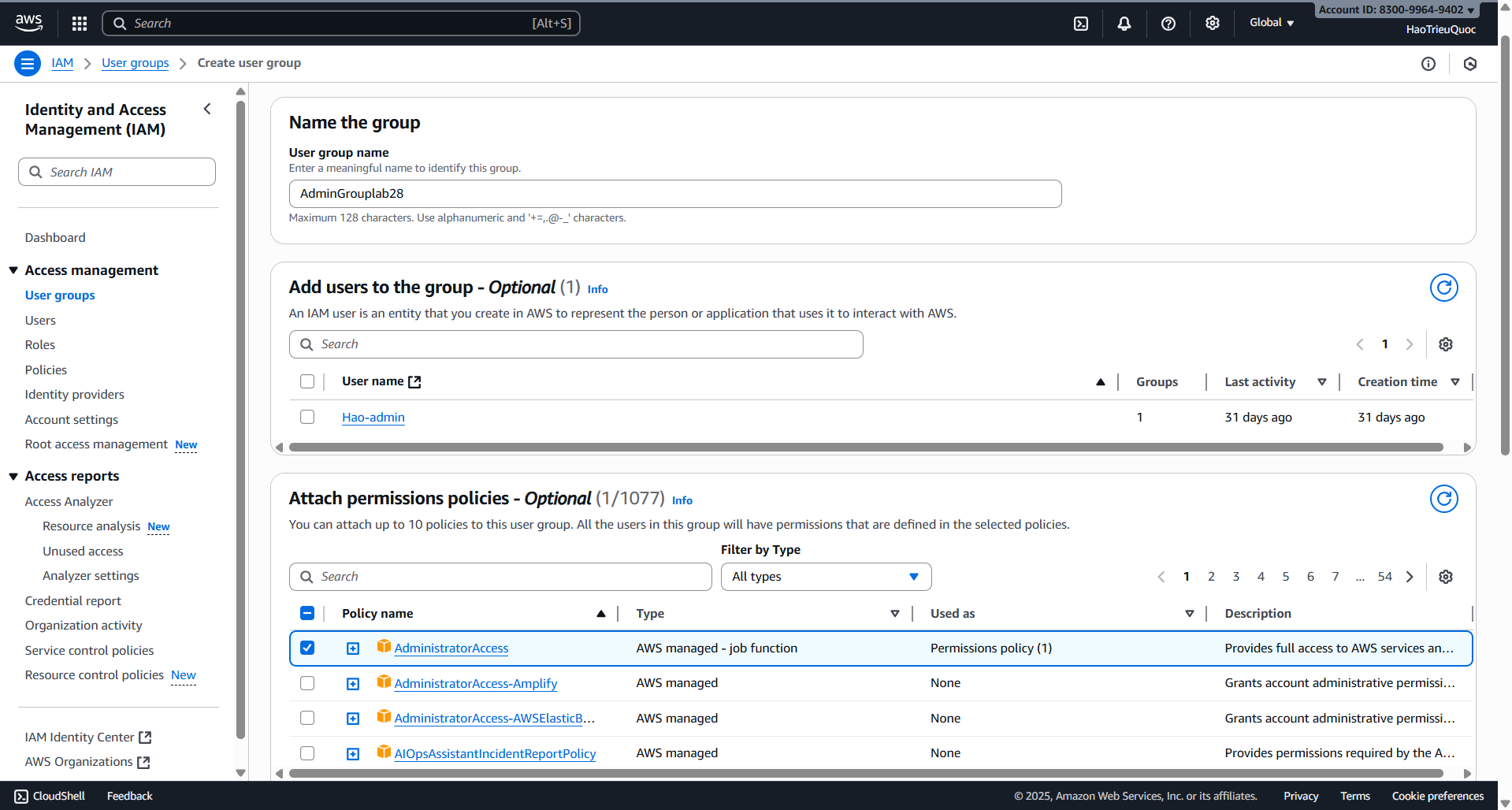
- Create User
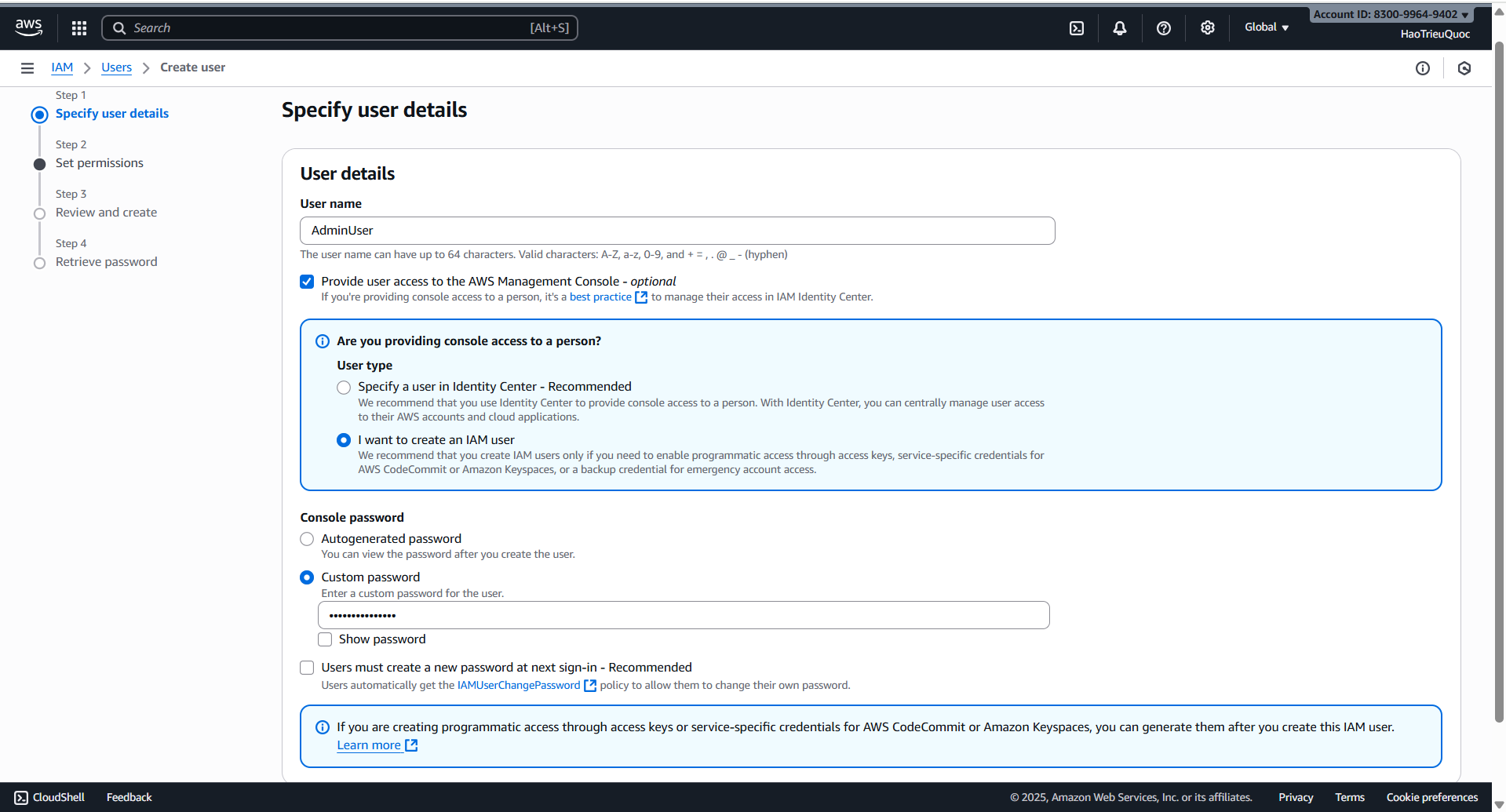
- Check User
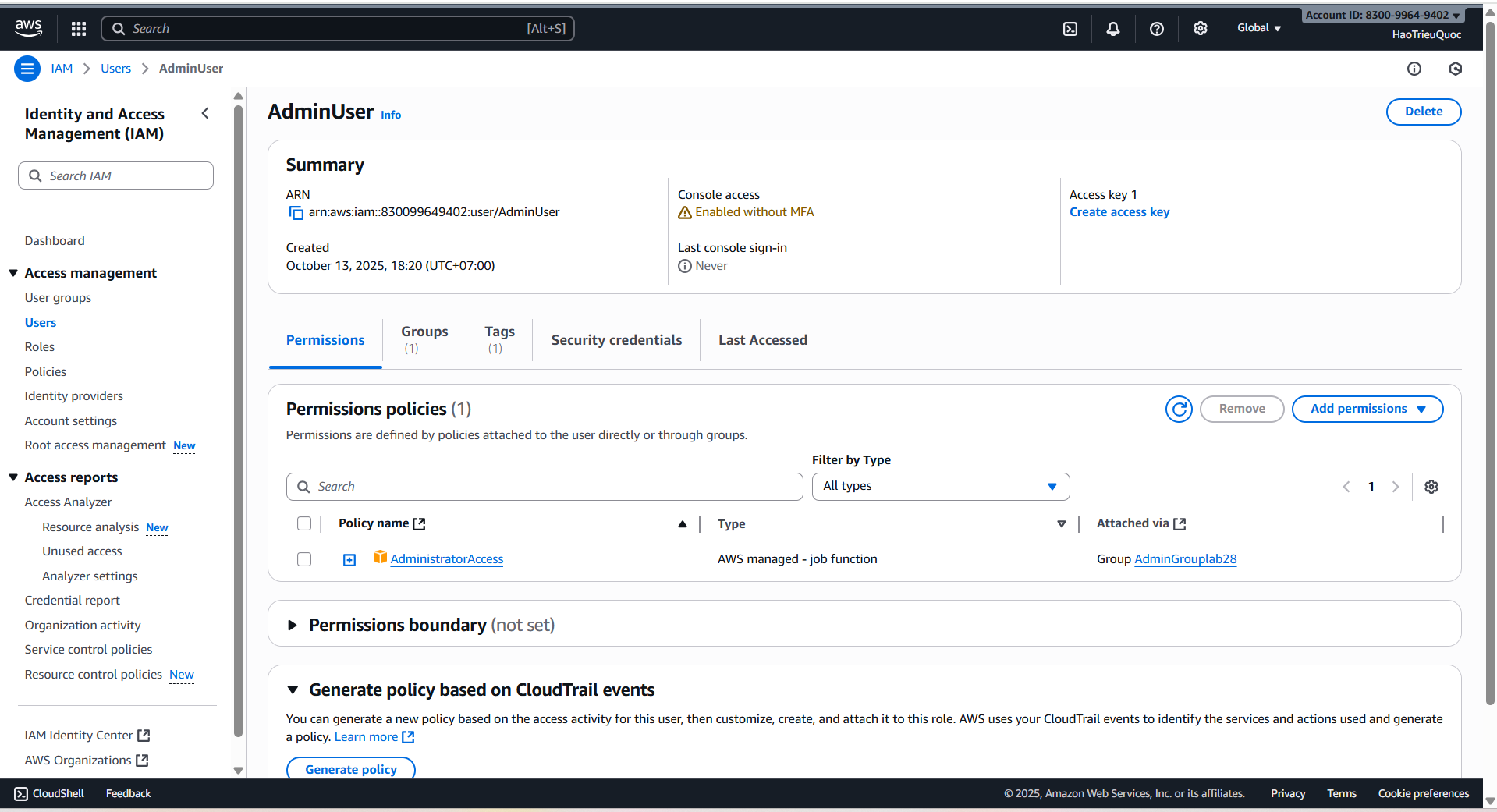
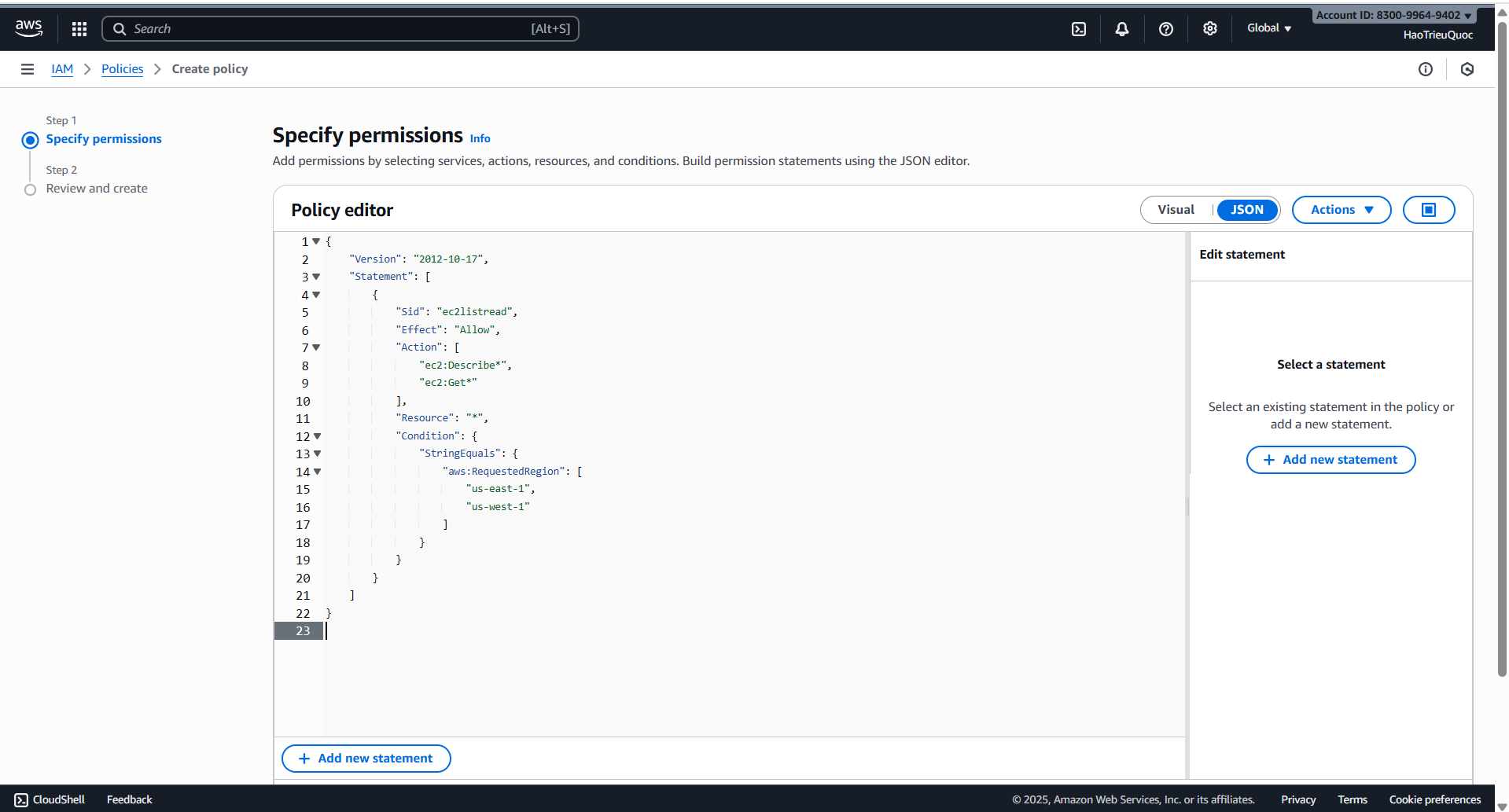
- Policy ec2-list-read
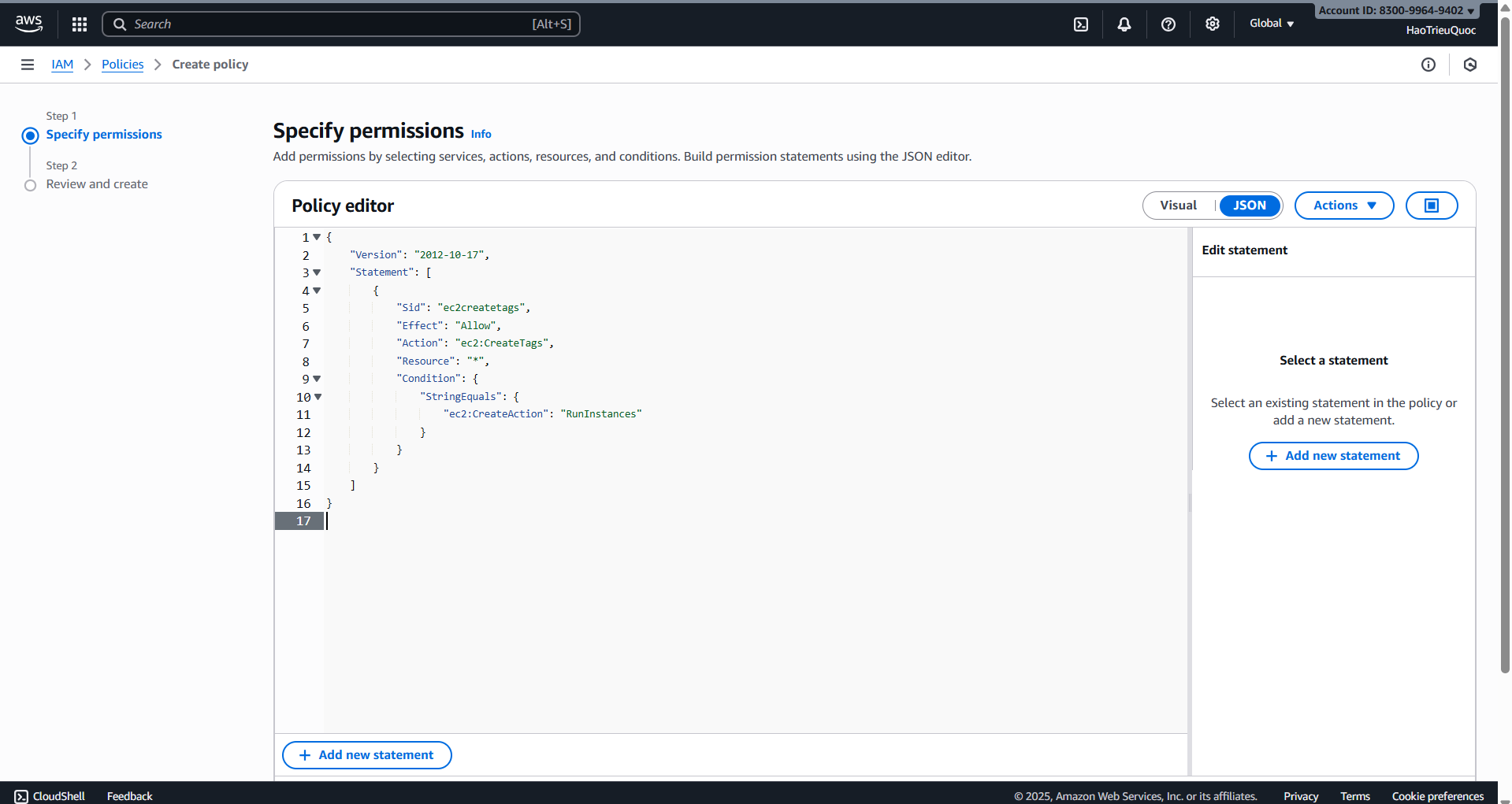
- Policy ec2-create-tags
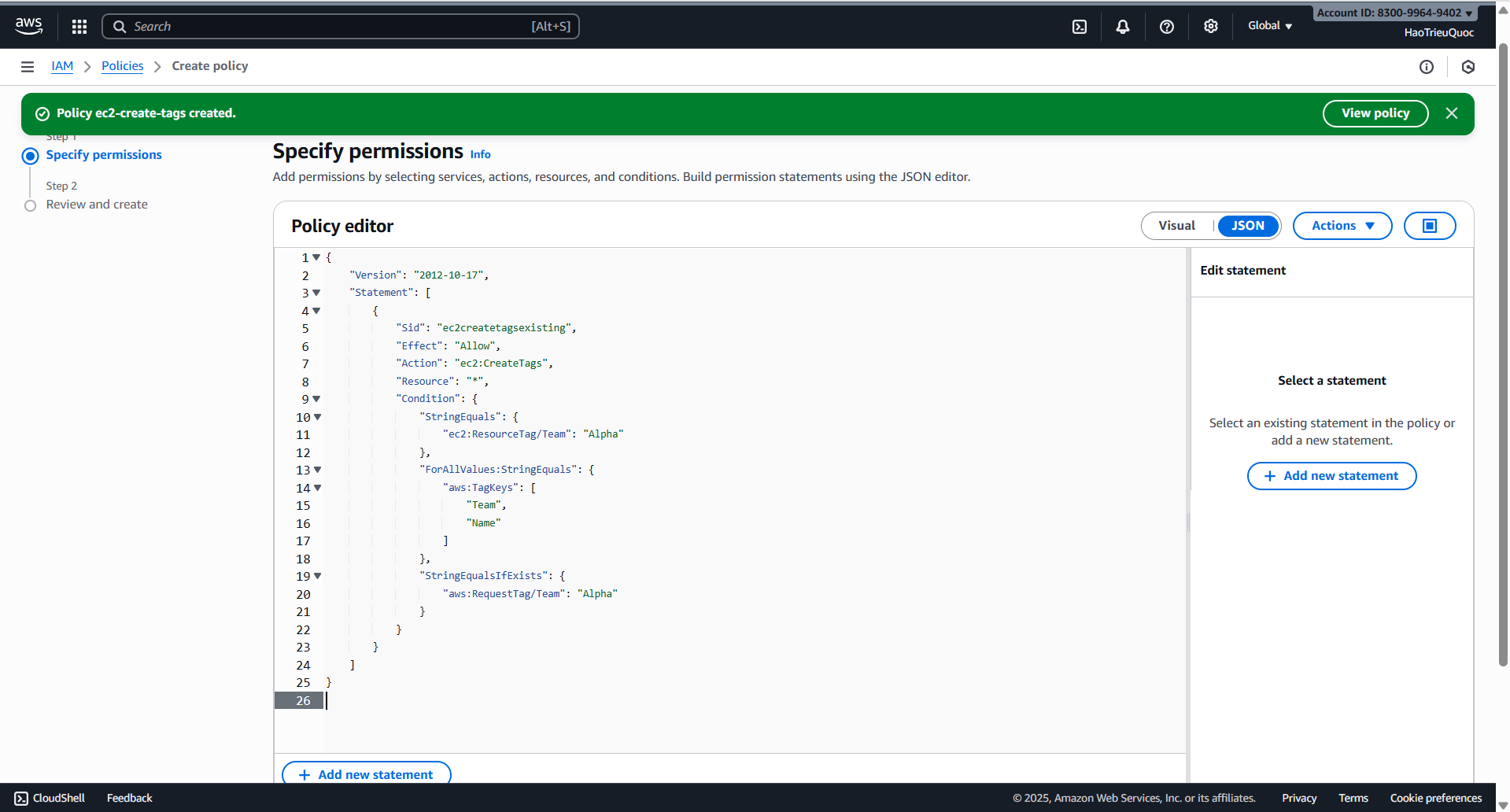
- Policy ec2-create-tags-existing
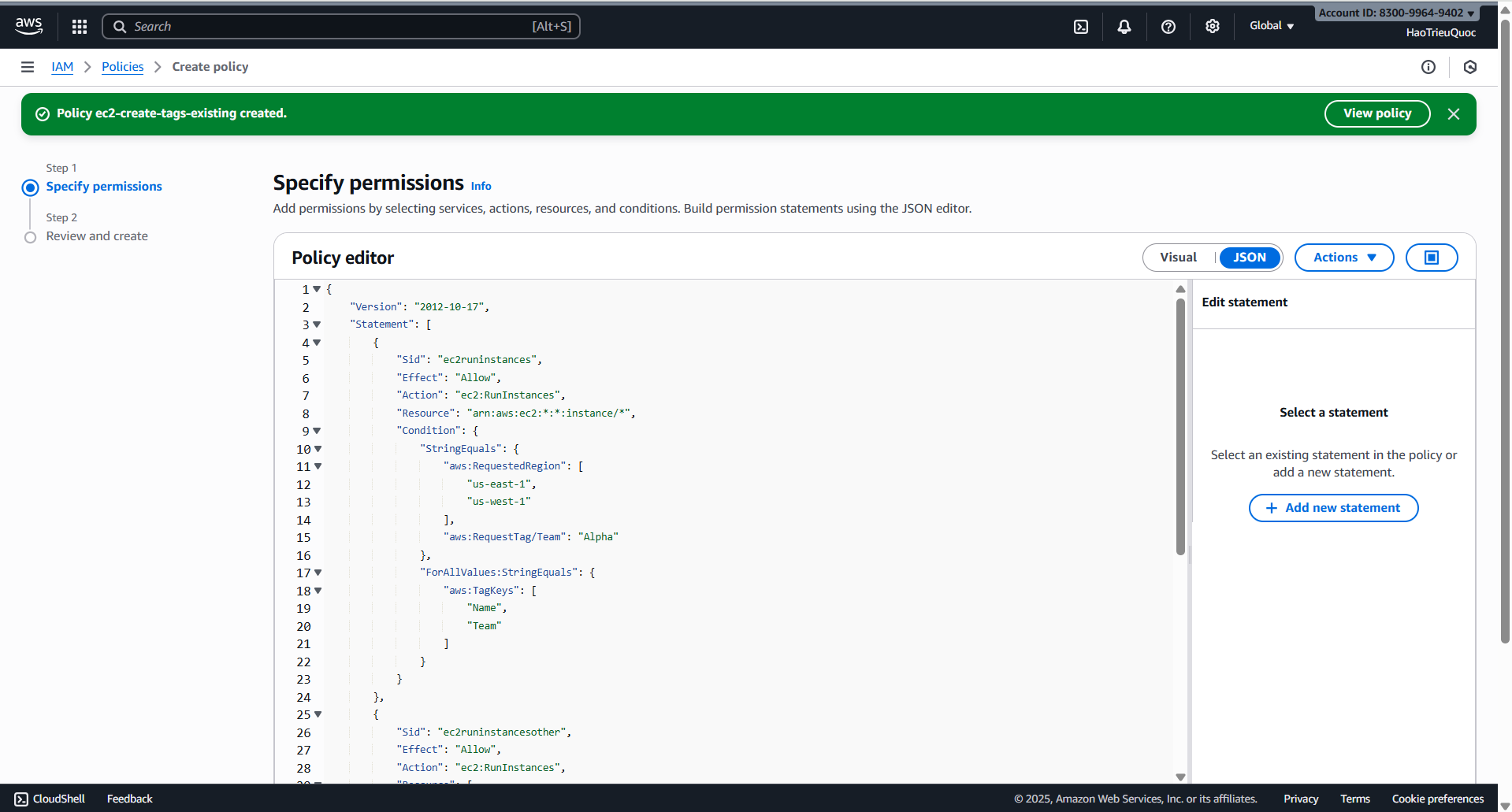
- Policy ec2-run-instances
- Policy ec2-manage-instances
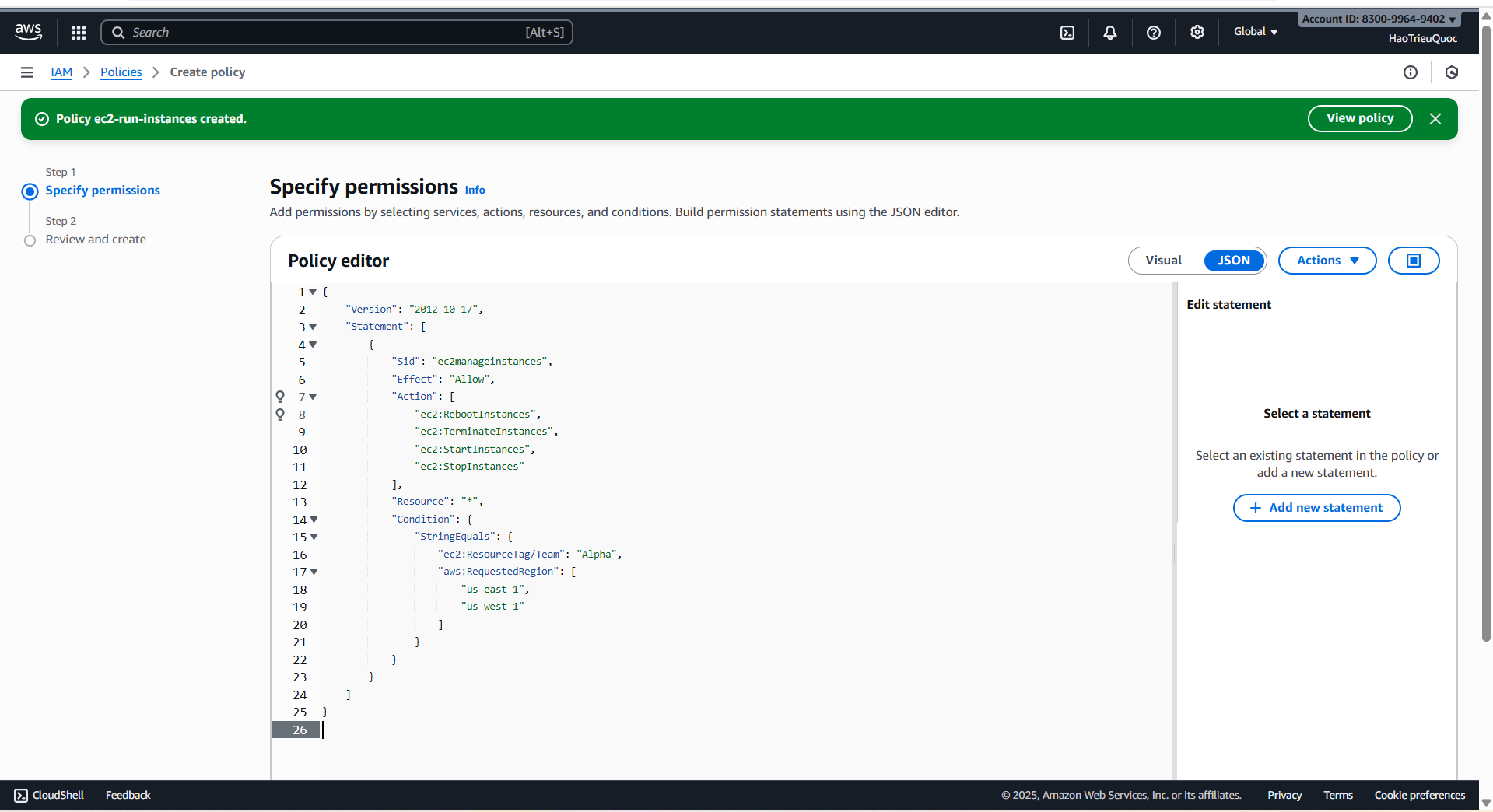
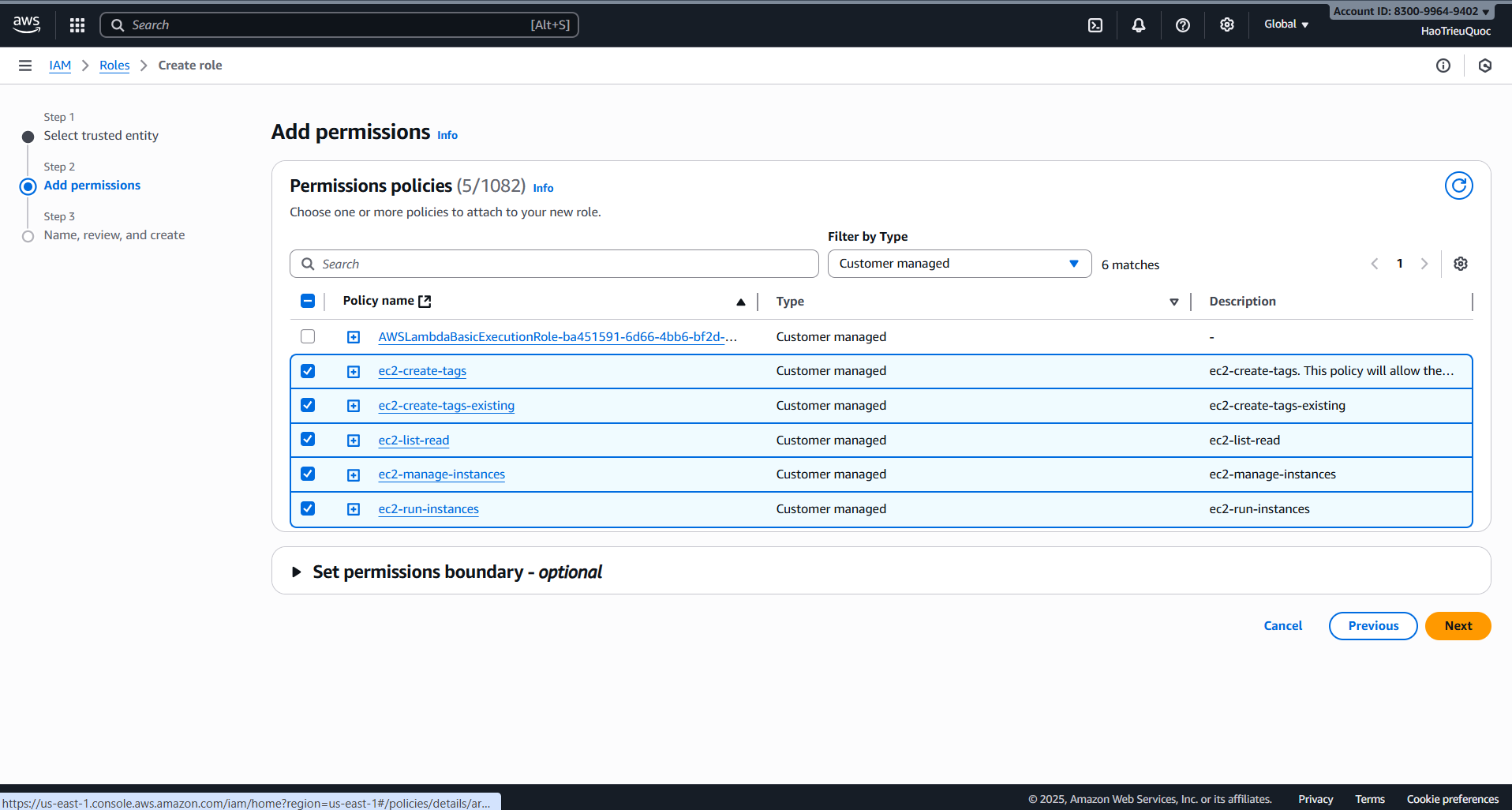
- Create role
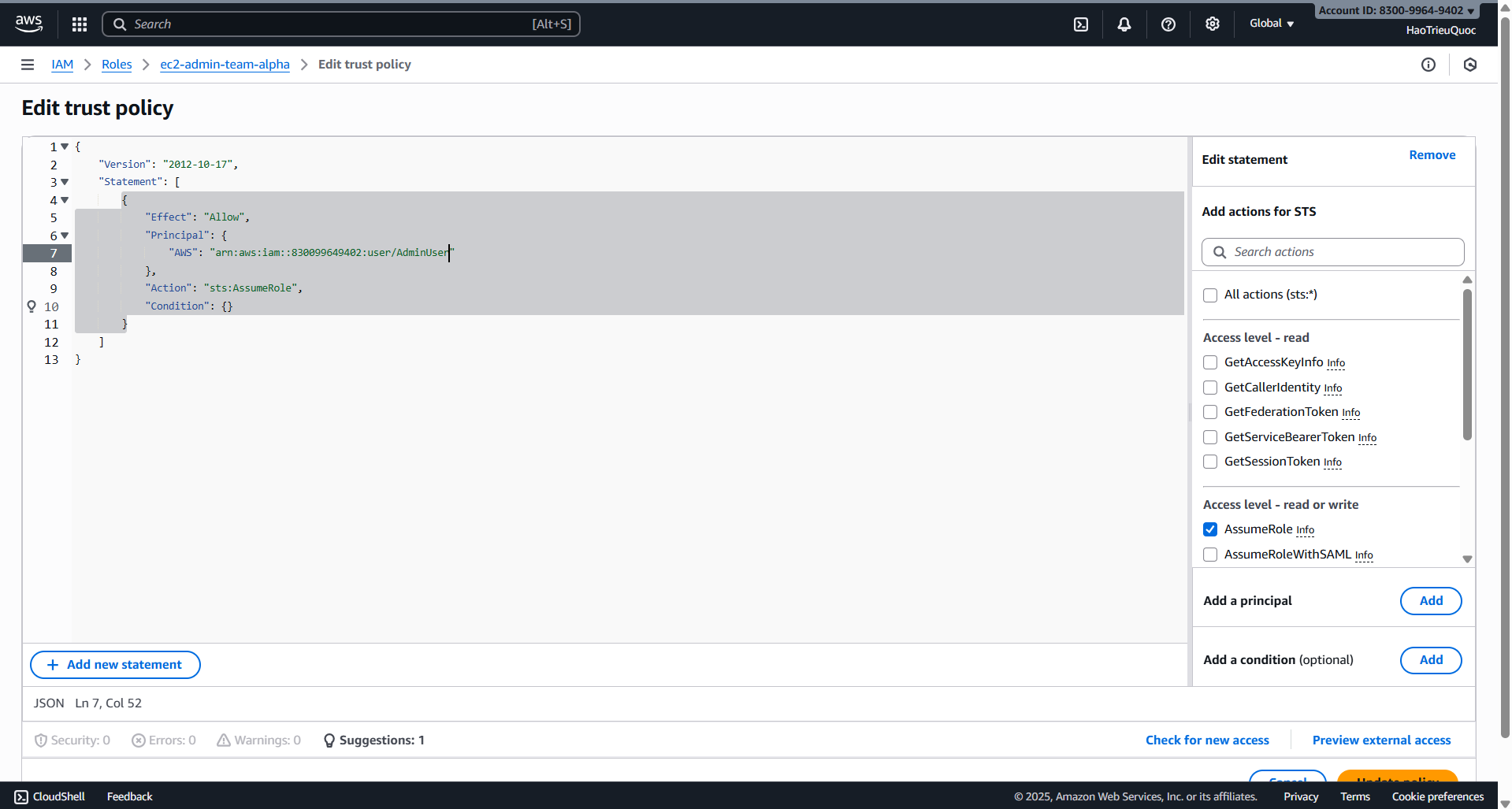
- Edit Trust Policy
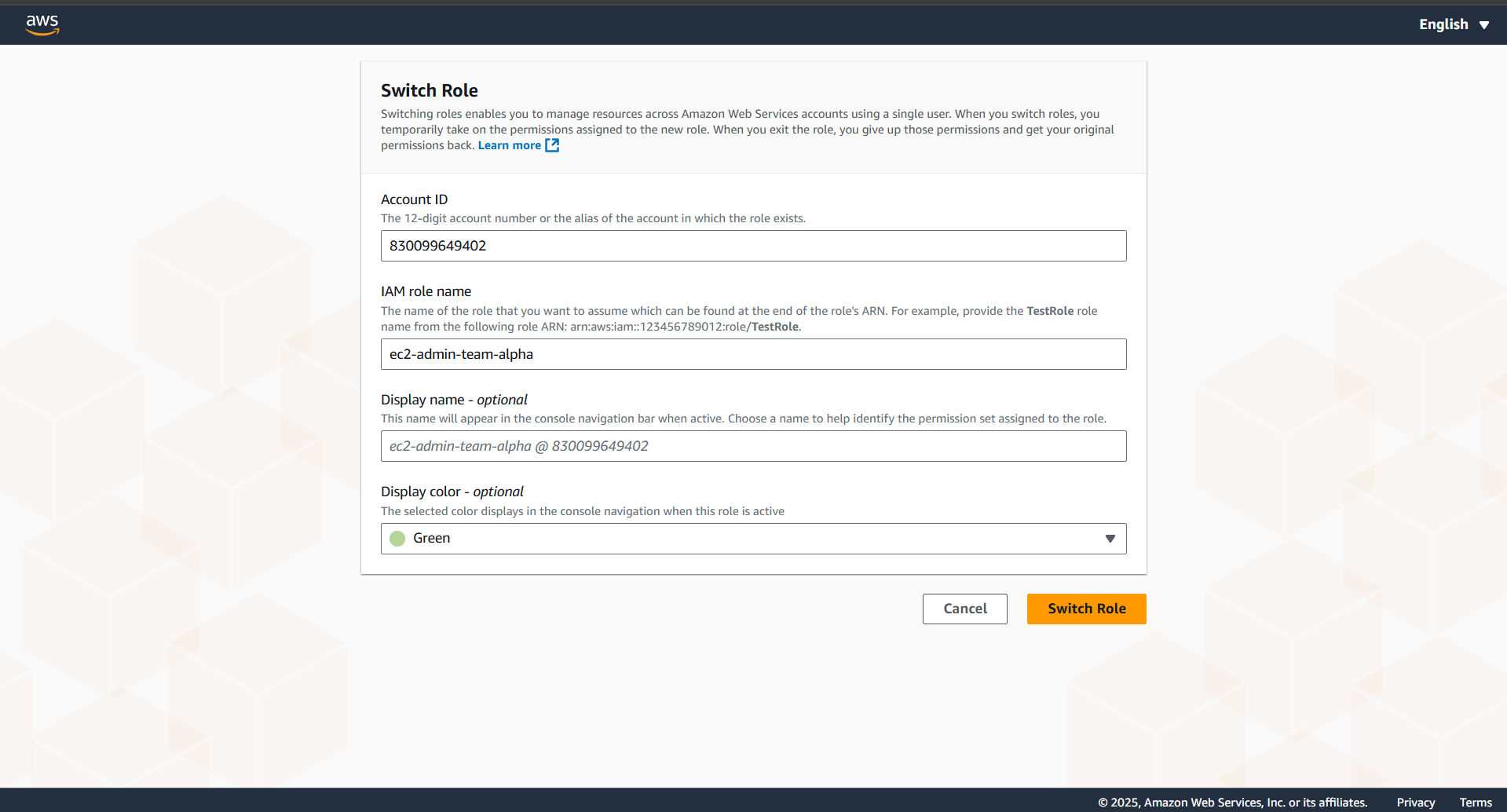
- Swich Role
- Create EC2 with tag name Beta
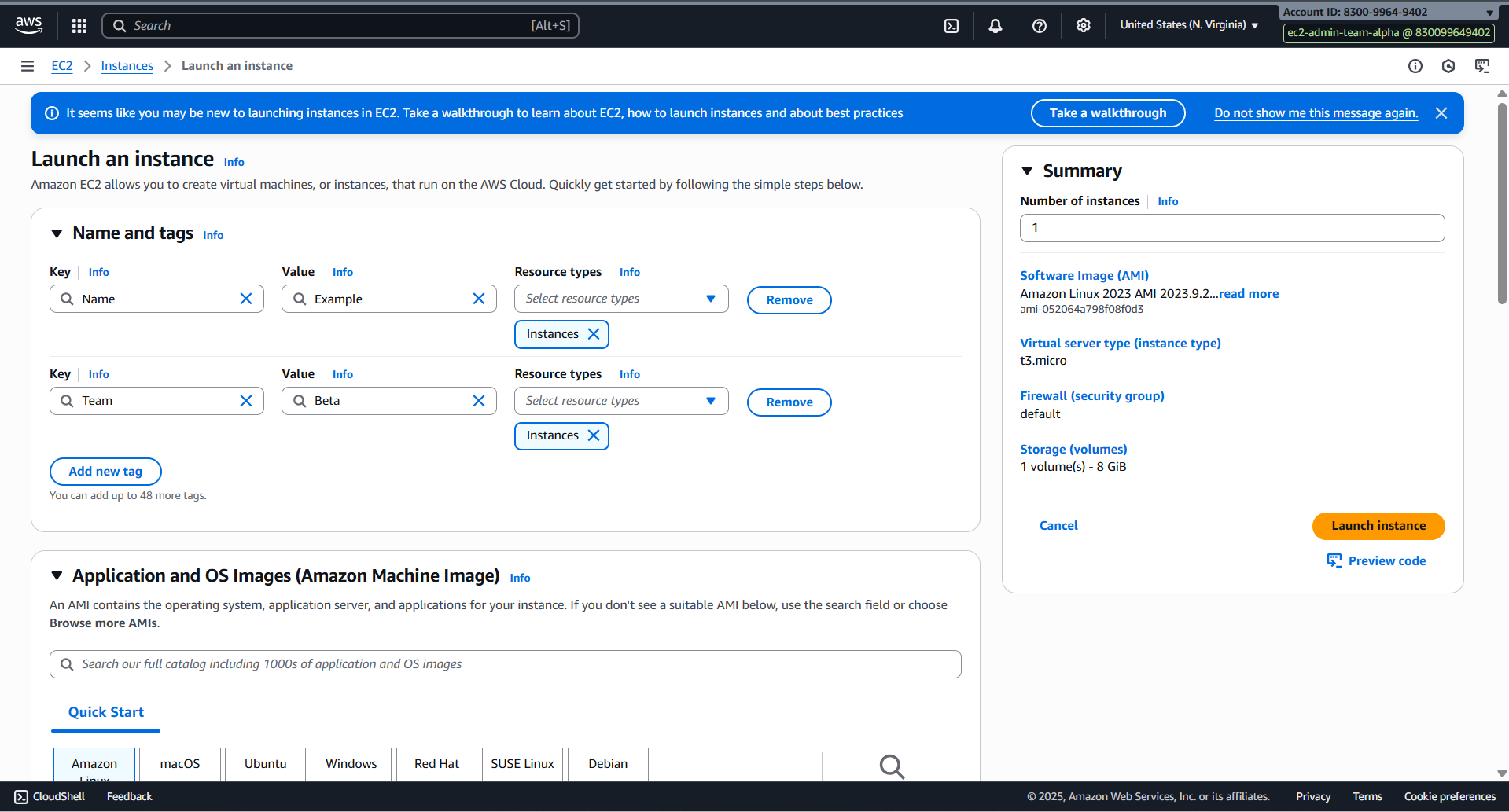
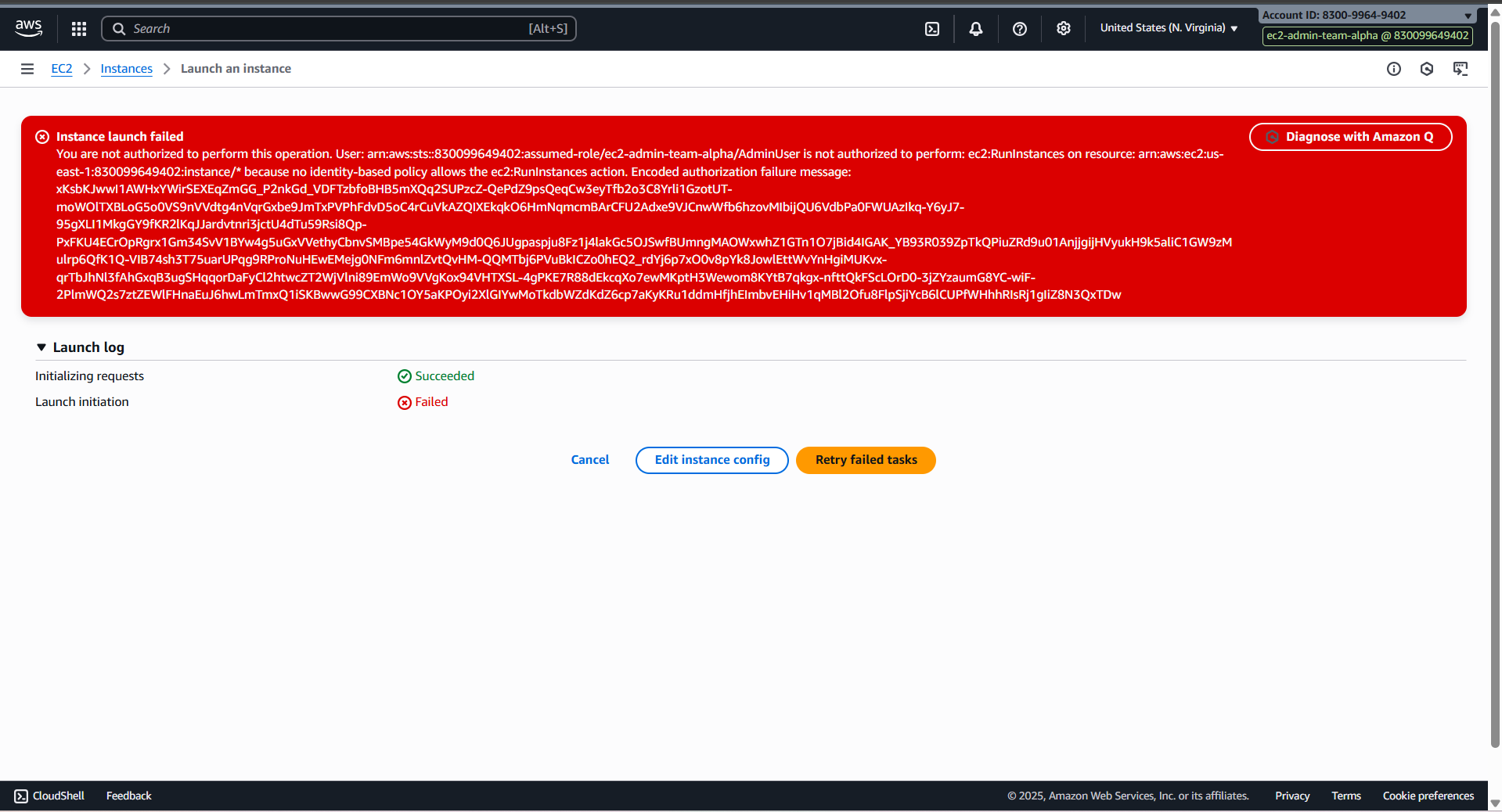
- Fail for the first time
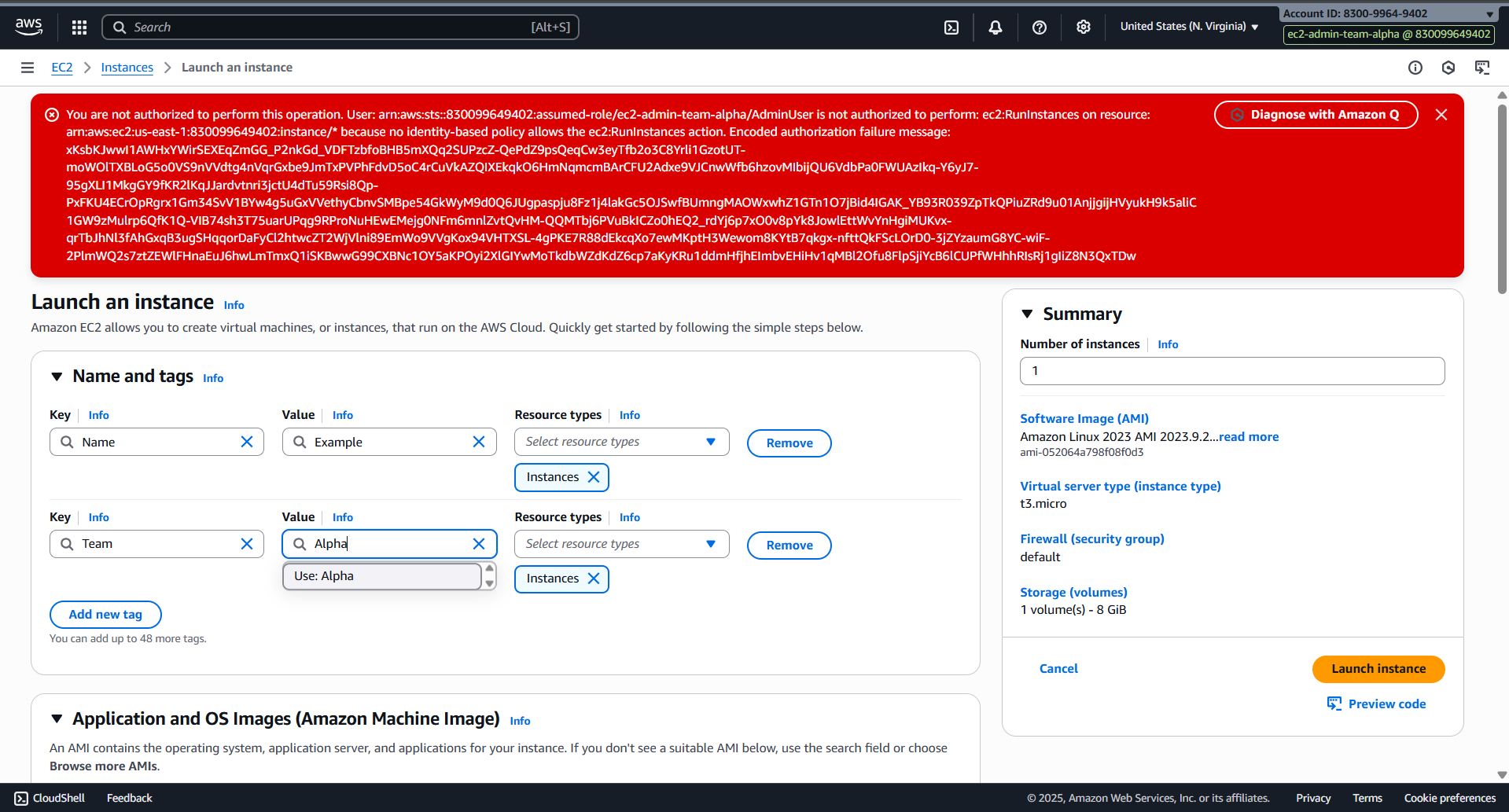
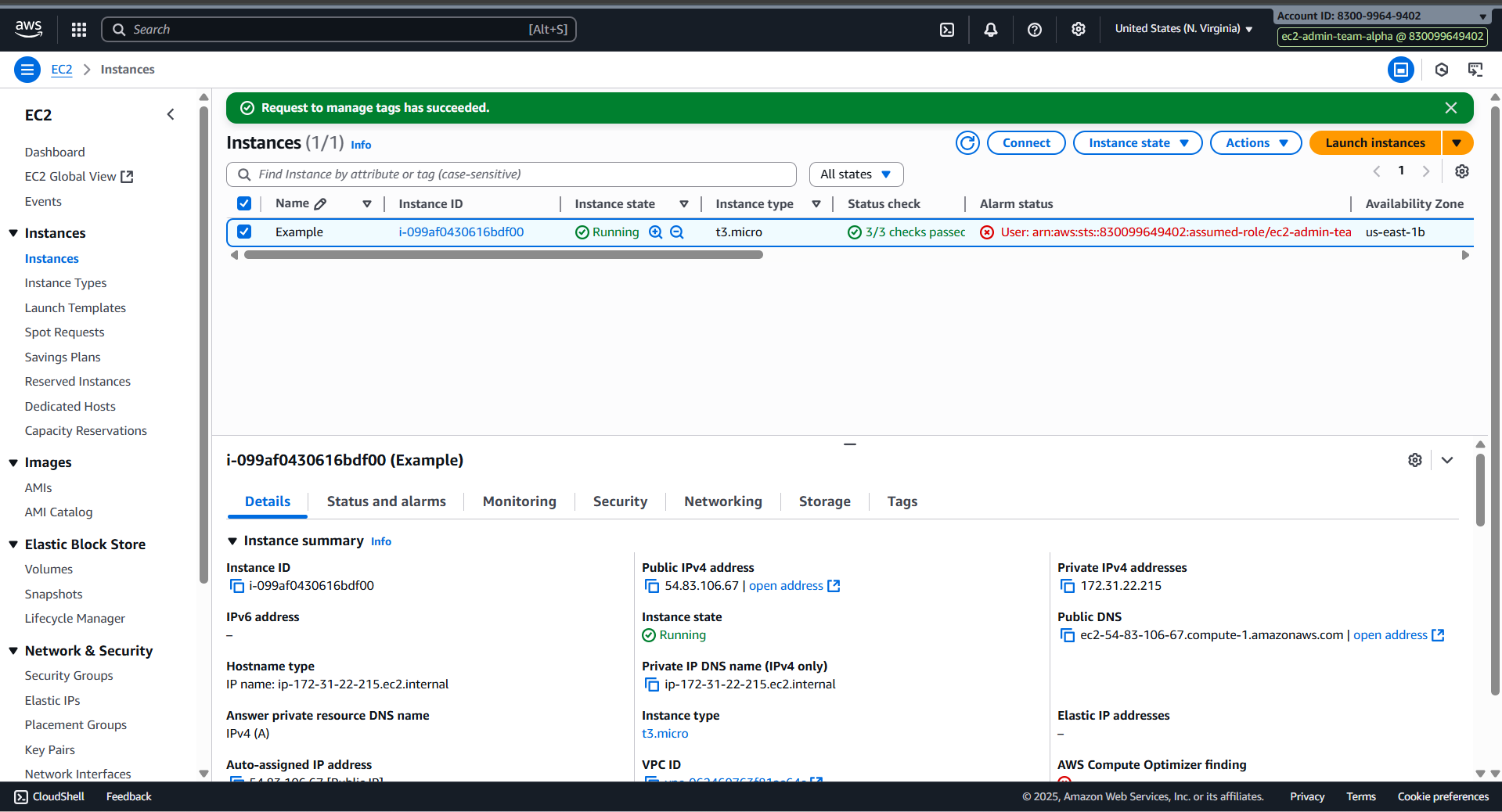
- Create EC2 with tag name Alpha
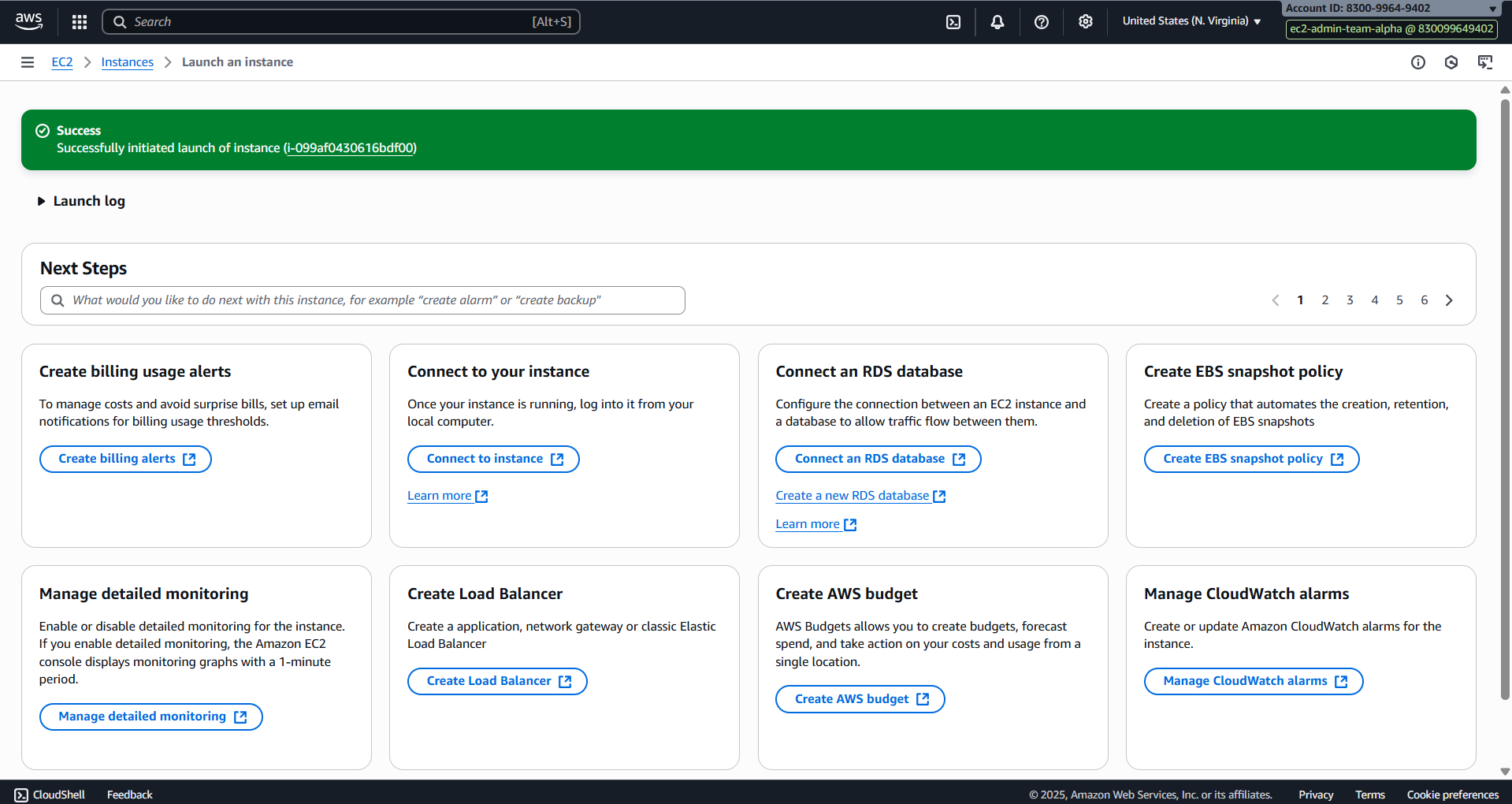
- Success for the second time
- Fail to edit tag name
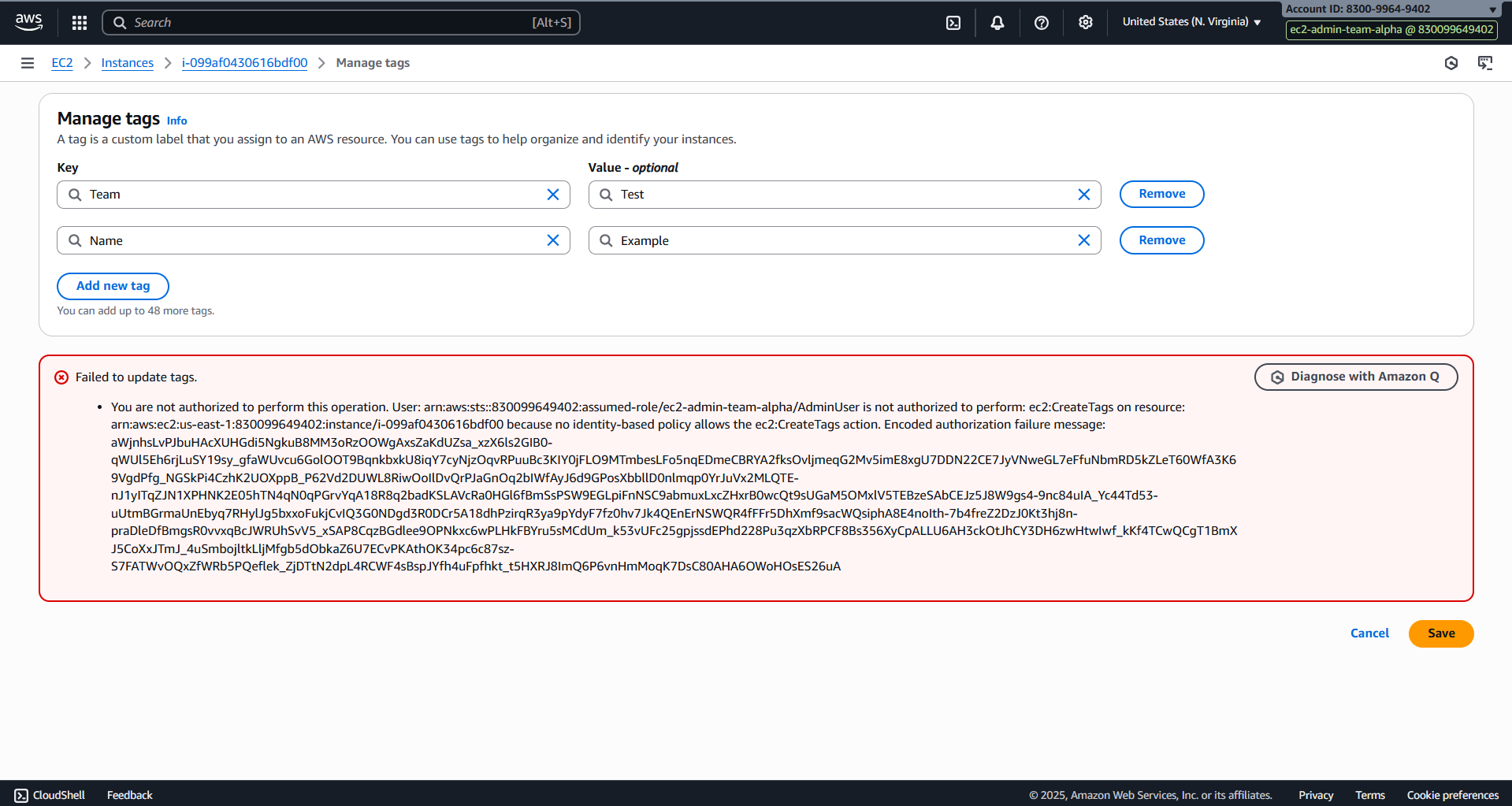
- Check policy
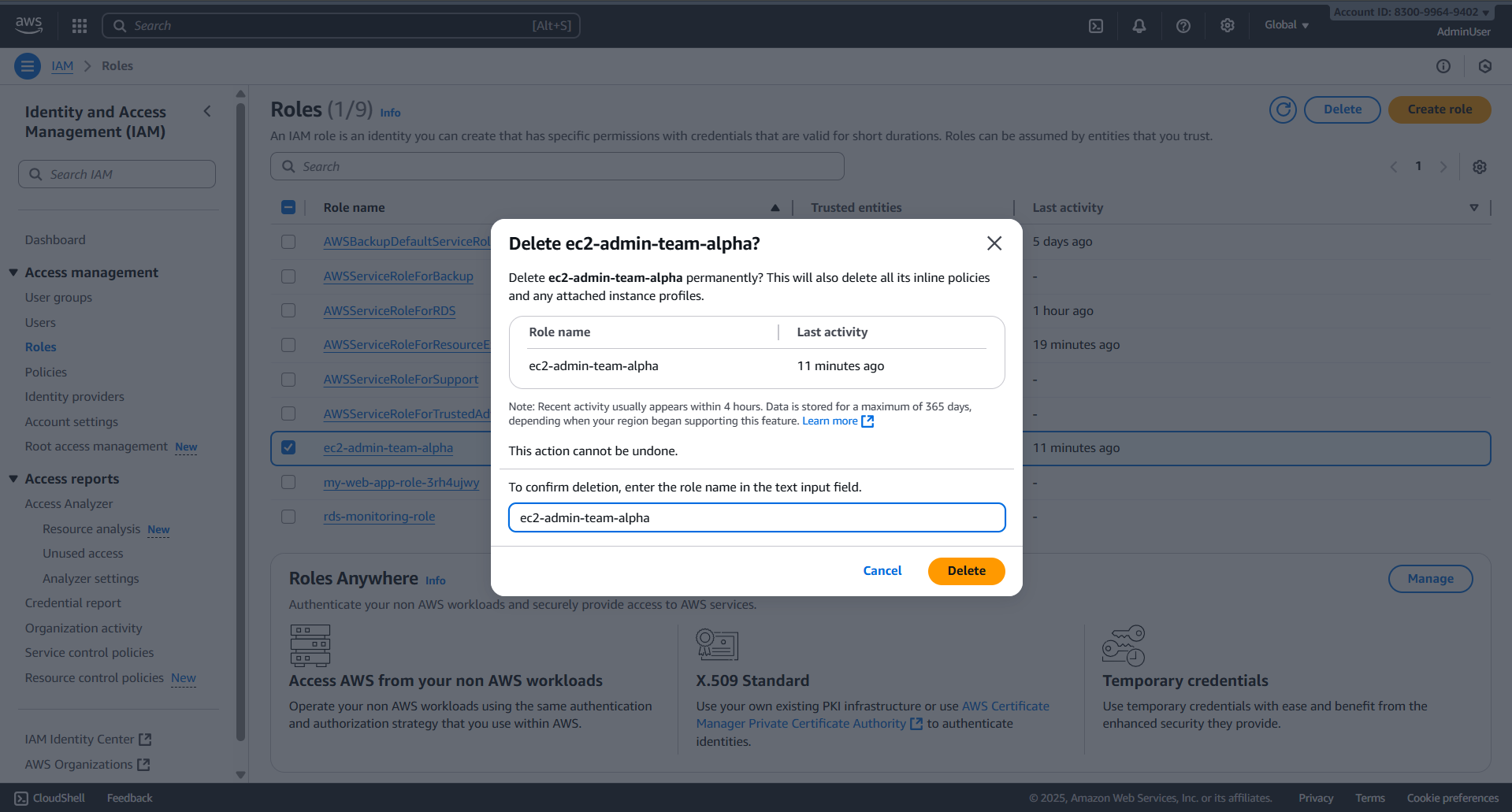
- Delete ec2-admin-team-alpha
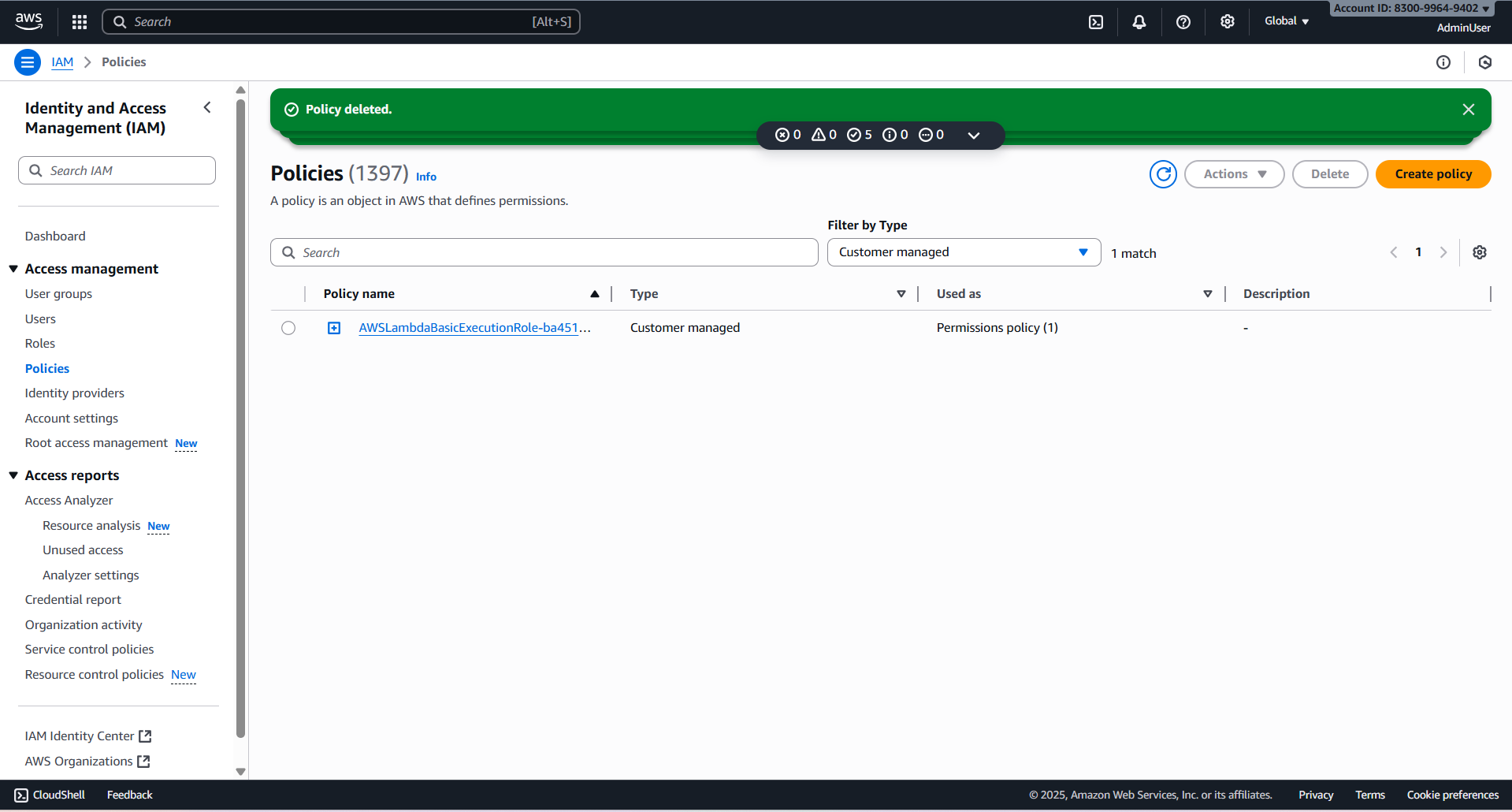
- Delete 5 policy
- Delete User
- Delete UserGroup